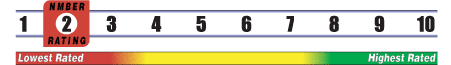
Four tablets contain: Dandelion root 320 mg • Bladderwrack root, stem, and leaf 320 mg • Buchu leaf 4:1 standardized extract 320 mg • Uva Ursi leaf 3:1 standardized extract 320 mg • Juniper berry 2:1 standardized extract 320 mg • Yellow Dock root 4:1 standardized extract 320 mg • Clivers leaf 4:1 standardized extract 320 mg • Burdock root and seed 320 mg • Parsley root and seed 300 mg • Barberry bark and root 60 mg. Other Ingredients: Di-Calcium Phosphate, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Vegetable Stearic Acid, Vegetable Magnesium Stearate, Food Glaze.
Brand name products often contain multiple ingredients. To read detailed information about each ingredient, click on the link for the individual ingredient shown above.
Below is general information about the effectiveness of the known ingredients contained in the product Aquaflow. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
There is insufficient reliable information available about the effectiveness of buchu.
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
There is insufficient reliable information available about the effectiveness of clivers.
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
There is insufficient reliable information available about the effectiveness of yellow dock.
Below is general information about the safety of the known ingredients contained in the product Aquaflow. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
LIKELY SAFE ...when the leaf is used in amounts commonly found in foods. Buchu has Generally Recognized As Safe status (GRAS) for use in foods in the US (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when the leaf is used orally and appropriately in medicinal amounts (2,12).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when excessive amounts of buchu leaf are taken orally or when the oil is ingested. Buchu contains pulegone, a known hepatotoxin (4). Pulegone is a major component of the oil. It is more abundant in buchu products that come from Agathosma crenulata (93681).
PREGNANCY: LIKELY UNSAFE
when used in medicinal amounts; buchu is reported to be an abortifacient (4).
LACTATION: POSSIBLY SAFE
when used in food amounts.
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of using larger amounts; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used in amounts commonly found in foods (12659,12660). Burdock root is commonly eaten as a vegetable (37422,92153,92154)
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used topically, short-term. An emulsion containing burdock fruit extract 1.2% has been safely applied to the face twice daily for 4 weeks (37420). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of burdock when used orally in supplemental doses.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately (12). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of clivers when used topically.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods. Dandelion has Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) status in the US (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately in medicinal amounts (12). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of dandelion when used topically.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using amounts greater than those in foods.
LIKELY SAFE ...when the fruit is consumed orally in food amounts (13527). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of European barberry when used orally in medicinal amounts or when used topically.
CHILDREN: LIKELY UNSAFE
when used orally in newborns.
The berberine constituent of European barberry can cause kernicterus in newborns, particularly preterm neonates with hyperbilirubinemia (2589). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of European barberry when used orally in older children.
PREGNANCY: LIKELY UNSAFE
when used orally.
Berberine is thought to cross the placenta and may cause harm to the fetus. Kernicterus has developed in newborn infants exposed to berberine (2589).
LACTATION: LIKELY UNSAFE
when used orally.
Berberine and other harmful constituents can be transferred to the infant through breast milk (2589).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when applied topically to the skin. A gel containing 1% Fucus vesiculosus extract, applied to the skin twice daily, has been used in clinical research with apparent safety for up to 5 weeks (12799).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally due to its iodine content and possible heavy metal content. Fucus vesiculosus contains up to 0.05% iodine or 226 mcg/gram dry weight (12789,74217). Ingesting more than 150 mcg of iodine daily can cause hyperthyroidism or exacerbate existing hyperthyroidism (12788). Fucus vesiculosus can also contain heavy metals, including cadmium, arsenic, and lead, and can cause heavy metal nephropathy (12789,12800,74213).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally because it may contain iodine and heavy metals (12789,74213,74217); avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods. Juniper, juniper berry, and juniper extract have Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status in the US (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used topically on limited areas of skin (12230). ...when the oil is used by inhalation and appropriately as aromatherapy (7107). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of juniper when used orally in doses of less than 10 grams of berries or 100 mg of oil daily, short-term. Juniper oil and berry have a long history of traditional use (12,103759).
LIKELY UNSAFE ...when used orally in excessive amounts or long-term. Use of daily doses greater than 10 grams of juniper berries (about 60 berries) or 100 mg of juniper essential oil, or prolonged oral use longer than 4 weeks, have been reported to increase the risk of severe adverse effects such as convulsions or kidney damage (8,19,103759).
PREGNANCY: UNSAFE
when used orally.
Juniper can increase uterine tone, interfere with fertility and implantation, and cause abortion (4,19).
LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods. Parsley has Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status in the US (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately in medicinal amounts, short-term (12,13173).
LIKELY UNSAFE ...when used orally in very large doses e., 200 grams). Parsley oil contains significant amounts of the potentially toxic constituents, apiole and myristicin (11). Apiole can cause blood dyscrasias, kidney toxicity, and liver toxicity; myristicin can cause giddiness and hallucinations (4). ...when parsley seed oil is used topically. Applying parsley seed oil to the skin can cause photodermatitis upon sun exposure (4). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of the topical use of parsley leaf and root.
PREGNANCY: LIKELY UNSAFE
when used orally in medicinal amounts.
Parsley has been used orally as an abortifacient and to stimulate menstrual flow (4,12,515,19104,92873). Population evidence suggests that maternal intake of An-Tai-Yin, an herbal combination product containing parsley and dong quai, during the first trimester increases the risk of congenital malformations of the musculoskeletal system, connective tissue, and eyes (15129).
LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately, short-term. Uva ursi has been used with apparent safety in doses of up to 3600 mg daily for 3-5 days (101815).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally long-term or in high doses. There is concern about the safety of long-term or high-dose use because of the hydroquinone content of uva ursi. Hydroquinone is thought to have mutagenic and carcinogenic effects (7). At high doses (around 20 grams of dried herb) it can cause convulsions, cyanosis, delirium, shortness of breath, and collapse. At very high doses (30 grams of dried herb or more) it can be fatal (4).
CHILDREN: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally by children.
Uva ursi contains hydroquinone and high tannin levels, which can cause severe liver problems in children (4,18); avoid using.
PREGNANCY: LIKELY UNSAFE
when used orally.
Uva ursi can have oxytocic effects, increasing the speed of labor (4,7,19); avoid using.
LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when properly prepared and consumed in amounts commonly found in foods. Young leaves must be boiled to remove the oxalate content; death has occurred after consuming uncooked leaves (6,18).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when the uncooked leaves are consumed. Young leaves must be boiled to remove the oxalate content; death has occurred after consuming uncooked leaves (6,18). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of properly prepared yellow dock when used orally in medicinal amounts.
PREGNANCY: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally; avoid using.
Yellow dock contains anthraquinone glycosides; unstandardized laxatives are not desirable during pregnancy (4).
LACTATION: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally; avoid using.
Anthraquinones are secreted into breast milk (4,5).
Below is general information about the interactions of the known ingredients contained in the product Aquaflow. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
Buchu may have antiplatelet effects (6002). Theoretically, buchu may enhance the effects of anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs and increase the risk of bleeding in some patients. Some anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs include aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix), dalteparin (Fragmin), enoxaparin (Lovenox), heparin, ticlopidine (Ticlid), warfarin (Coumadin), and others.
|
Buchu contains pulegone, a known hepatotoxin (4,93681). There is some concern that buchu may adversely affect the liver, especially when the leaf is used in large doses or the oil is ingested (93681). Theoretically, concomitant use with hepatotoxic drugs might increase the risk of liver damage. Some of these drugs include acarbose (Precose, Prandase), amiodarone (Cordarone), atorvastatin (Lipitor), azathioprine (Imuran), carbamazepine (Tegretol), cerivastatin (Baycol), diclofenac (Voltaren), felbamate (Felbatol), fenofibrate (Tricor), fluvastatin (Lescol), gemfibrozil (Lopid), isoniazid, itraconazole, (Sporanox), ketoconazole (Nizoral), leflunomide (Arava), lovastatin (Mevacor), methotrexate (Rheumatrex), nevirapine (Viramune), niacin, nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin), pioglitazone (Actos), pravastatin (Pravachol), pyrazinamide, rifampin (Rifadin), ritonavir (Norvir), rosiglitazone (Avandia), simvastatin (Zocor), tacrine (Cognex), tamoxifen, terbinafine (Lamisil), valproic acid, and zileuton (Zyflo)
|
Buchu is thought to have diuretic properties (93681). Theoretically, buchu might reduce excretion and increase levels of lithium. The dose of lithium might need to be decreased.
|
Theoretically, taking burdock with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs might increase the risk of bleeding.
In vitro research shows that lignans from burdock reduce rabbit platelet aggregation by inhibiting platelet activating factor (12619). This interaction has not been reported in humans. |
Theoretically, taking dandelion root along with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
In vitro research suggests that dandelion root inhibits platelet aggregation (18291).
|
Theoretically, dandelion might increase the risk for hypoglycemia when used with antidiabetes drugs.
Laboratory research suggests that dandelion extract may have moderate alpha-glucosidase inhibitor activity and might also increase insulin secretion (13474,90926). Also, in a case report, a 58-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes who was being treated with insulin developed hypoglycemia 2 weeks after beginning to eat salads containing dandelion (46960).
|
Theoretically, dandelion might increase levels of drugs metabolized by CYP1A2.
Laboratory research suggests that dandelion might inhibit CYP1A2 (12734). So far, this interaction has not been reported in humans. However, until more is known, watch for an increase in the levels of drugs metabolized by CYP1A2 in patients taking dandelion.
|
Theoretically, dandelion might increase the clearance of drugs that are UDP-glucuronosyltransferase substrates.
There is some preliminary evidence that dandelion might induce UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, a phase II enzyme (12734).
|
Theoretically, through diuretic effects, dandelion might reduce excretion and increase levels of lithium.
Animal research suggests that dandelion has diuretic properties (13475). As diuretics can increase serum lithium levels, the dose of lithium might need to be decreased when taken with dandelion.
|
Theoretically, dandelion might increase the risk of hyperkalemia when taken with potassium-sparing diuretics.
Dandelion contains significant amounts of potassium (13465).
|
Theoretically, dandelion might lower fluoroquinolone levels.
Animal research shows that dandelion reduces absorption of ciprofloxacin and can lower levels by 73% (13477). However, this effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, taking European barberry with anticholinergic drugs might cause additive effects.
In vitro evidence suggests that European barberry might have anticholinergic properties (13527).
|
Theoretically, European barberry may increase the risk of bleeding if used with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
|
Theoretically, taking European barberry with antidiabetes drugs might increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Preliminary clinical evidence suggests that European barberry juice reduces fasting glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes who are also taking antidiabetes drugs (98575). Additionally, some animal studies show that berberine, a constituent of European barberry, has antiglycemic potential (33622,33667). Monitor blood glucose levels closely.
|
Theoretically, taking European barberry with antihypertensive drugs might increase the risk of hypotension.
|
Theoretically, taking European barberry with cholinergic drugs might decrease the effects of cholinergic drugs.
In vitro evidence suggests that European barberry might have anticholinergic properties (13527).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use with drugs that have sedative properties may cause additive effects.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use with cyclosporine may cause additive effects.
Berberine, a constituent of European barberry, can reduce the metabolism and increase serum levels of cyclosporine. This effect is attributed to the ability of berberine to inhibit cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), which metabolizes cyclosporine (13524). Theoretically, European barberry might have a similar effect.
|
Theoretically, European barberry might increase the levels and clinical effects of CYP3A4 substrates.
There is very preliminary evidence suggesting that berberine, a constituent of European barberry, might inhibit the CYP3A4 enzyme (13524). Theoretically, European barberry might have a similar effect.
|
Theoretically, combining Fucus vesiculosus with amiodarone might cause excessively high iodine levels.
|
Theoretically, taking Fucus vesiculosus with antiplatelet or anticoagulant drugs might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
|
Due to its iodine content, Fucus vesiculosus might alter the effects of antithyroid drugs.
Fucus vesiculosus contains high concentrations of iodine (7135). Iodine in high doses has been reported to cause both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, depending on the individual's past medical history. Taking Fucus vesiculosus while using antithyroid drugs could alter the effects of the antithyroid drugs (2138,17574).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use of Fucus vesiculosus with CYP2C8 substrates might increase the risk for adverse effects.
In vitro research shows that fucoidan, a constituent of Fucus vesiculosus, inhibits CYP2C8 (97791). This interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use of Fucus vesiculosus with CYP2C9 substrates might increase the risk for adverse effects.
In vitro research shows that fucoidan, a constituent of Fucus vesiculosus, inhibits CYP2C9 (97791). This interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use of Fucus vesiculosus with CYP2D6 substrates might alter the effects of these substrates.
In vitro research shows that fucoidan, a constituent of Fucus vesiculosus, both inhibits and induces CYP2D6 (97791). This interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use of Fucus vesiculosus with CYP3A4 substrates might increase the risk for adverse effects.
In vitro research shows that fucoidan, a constituent of Fucus vesiculosus, inhibits CYP3A4 (97791). This interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Concomitant use of Fucus vesiculosus and lithium has resulted in hyperthyroidism.
There is a case of hyperthyroidism occurring in a patient taking Fucus vesiculosus and lithium (74217). Monitor thyroid hormones closely in patients taking lithium and Fucus vesiculosus concomitantly.
|
Due to its iodine content, Fucus vesiculosus might alter the effects of thyroid hormone.
Fucus vesiculosus contains high concentrations of iodine (7135). Iodine in high doses has been reported to cause both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, depending on the individual's past medical history. Taking Fucus vesiculosus while using thyroid hormone could alter the effects of thyroid hormone.
|
Theoretically, taking juniper berry with antidiabetes medications might cause additive hypoglycemia.
|
Theoretically, juniper berry might increase the risk of adverse effects from diuretic drugs.
|
Theoretically, juniper berry might reduce lithium excretion and increase serum levels of lithium.
|
Theoretically, parsley might increase the risk of bleeding when taken with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
Animal research suggests that parsley has antiplatelet effects (68209).
|
Theoretically, parsley might increase the risk of hypoglycemia when taken with antidiabetes drugs.
|
Theoretically, aspirin might increase the severity of allergic reactions to parsley.
In one case, severe urticaria and swelling were reported after taking aspirin with parsley in an individual with a known mild parsley allergy (5054).
|
Theoretically, parsley might increase serum levels of CYP1A2 substrates.
Laboratory research suggests that parsley can inhibit CYP1A2 (68176).
|
Theoretically, parsley might enhance or interfere with the effects of diuretic drugs.
|
Theoretically, parsley might increase the duration of pentobarbital effects.
Animal research suggests that parsley juice prolongs the action of pentobarbital, perhaps by decreasing cytochrome P450 levels (25362). It is not known if this occurs in humans or if this applies to other barbiturates or sedatives.
|
Theoretically, large quantities of parsley might increase sirolimus levels.
In one case report, an adult female with a history of kidney transplant presented with elevated blood sirolimus levels, approximately 4-7 times greater than previous measures, after daily consumption of a juice containing approximately 30 grams of parsley for 7 days. Sirolimus levels returned to normal a week after the parsley juice was discontinued (106010).
|
Theoretically, large amounts of parsley leaf and root might decrease the effects of warfarin.
Parlsey contains vitamin K (19).
|
Theoretically, uva ursi may decrease the metabolism of CYP2C19 substrates.
In vitro, uva ursi appears to inhibit cytochrome CYP2C19 (98550). This effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, uva ursi may decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 substrates.
In vitro, uva ursi appears to inhibit CYP3A4 (98550). This effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, uva ursi may increase levels of drugs metabolized by glucuronidation.
In vitro, uva ursi extract appears to strongly inhibit UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A1 (UGT1A1). However, uva ursi extract does not appear to inhibit UGT1A1 in animal models (98549). This effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, uva ursi may increase lithium levels, necessitating a decrease in dose.
Uva ursi may have diuretic properties (81637). Diuretics may increase lithium reabsorption with sodium in the proximal tubule of the kidney. Theoretically, uva ursi might reduce excretion and increase levels of lithium.
|
Theoretically, uva ursi may alter the levels of drugs transported by P-glycoprotein.
In vitro, uva ursi appears to inhibit the multi-drug transporter protein, P-glycoprotein (98550). This effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Effects of uva ursi in the urinary tract may be reduced by urinary acidifying agents.
Uva ursi seems to work best in alkaline urine. Theoretically, taking uva ursi with medications known to acidify the urine may decrease any effects of uva ursi on the urinary tract (19).
|
Theoretically, yellow dock might increase the risk of digoxin toxicity when used long-term or in large amount.
|
Theoretically, yellow dock might increase the risk of hypokalemia when taken with diuretics.
|
Theoretically, the laxative effects of yellow dock might increase the effects of warfarin, including the risk of bleeding.
|
Below is general information about the adverse effects of the known ingredients contained in the product Aquaflow. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
General ...Orally, buchu leaf can cause GI and kidney irritation (4,6) and increase menstrual flow (6). Buchu is also a reported abortifacient (4).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, buchu may cause gastrointestinal irritation (4,6).
Genitourinary ...Orally, buchu may increase menstrual flow (6). Buchu is also a reported abortifacient (4).
General
...Orally, burdock is well tolerated when consumed as a food.
Although a thorough evaluation of safety outcomes is lacking, there has been long-standing historical use of burdock with few noted adverse effects.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
All ROAs: Allergic reactions, including contact dermatitis and anaphylaxis.
Dermatologic ...Contact dermatitis has been reported secondary to burdock, especially after prolonged use of the root oil (37422). There are cases of allergic dermatitis secondary to using burdock plasters. Two males and a 14 year-old female developed erythematous and vesicular, pruritic, and exudative reactions in areas corresponding to the application of burdock root plasters (12667). Reactions occurred up to 7 days after initial use. Patch testing was positive for burdock sensitivity in all three patients and was nonreactive in matched controls.
Hematologic ...In one case report, a 38-year-old female developed immune-mediated thrombocytopenia after consuming a "cleansing" tea containing unknown amounts of burdock and yellow dock. The patient presented with bruising, mild weakness, and fatigue, which started 2-3 days after consuming the tea, and was found to have a platelet count of 5,000 per mcL. Symptoms resolved after platelet transfusion and treatment with oral dexamethasone (108971). It is unclear if these effects were caused by burdock, yellow dock, the combination, or other contributing factors.
Hepatic ...A case of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver disease (DILI) is reported in a 36-year-old female who presented with abdominal pain after 1 month of taking an herbal liver detox tea containing burdock and other ingredients. Remarkable laboratory values included elevated liver enzymes, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin. The patient received a loading dose of N-acetylcysteine and was hospitalized for 12 days (112178). However, it is unclear if the adverse effect was due to burdock, other ingredients, or the combination.
Immunologic ...There is one case of anaphylactic shock secondary to eating boiled burdock. One hour after eating boiled burdock the patient presented with redness over the entire body and dyspnea. He was found to have low blood pressure and was treated with subcutaneous epinephrine 1 mg and intravenous lactated ringer's solution containing hydrocortisone 100 mg and dexamethasone 8 mg. The cause of anaphylactic shock was attributed to allergenicity to burdock based on positive skin prick test results. Previously, the patient had experienced urticaria after eating boiled burdock (12660).
Neurologic/CNS ...Anticholinergic reactions including dry mouth, dizziness, blurred vision, weakness, dilated pupils, inability to urinate, and bradycardia have been reported following the consumption of burdock products (12662,37421,37431,37434,37435). However, these anticholinergic reactions are believed result from contamination of burdock with belladonna alkaloids. Burdock itself does not contain atropine or other constituents that would be responsible for these reactions.
General ...Orally, clivers seems to be well tolerated. However, a thorough evaluation of safety outcomes has not been conducted.
General
...Orally, dandelion seems to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Diarrhea, heartburn, and stomach discomfort.
Topically: Dermatitis in sensitive individuals.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Anaphylaxis in sensitive individuals.
Cardiovascular ...In one report, a 39-year-old obese woman developed palpitations and syncope after taking a weight loss supplement containing a combination of dandelion, bladderwrack, and boldo for 3 weeks. The patient was found to have prolonged QT-interval on ECG and frequent episodes of sustained polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (14321). It is not clear whether dandelion, another ingredient, or the combination of ingredients is responsible for this adverse effect. The product was not analyzed to determine the presence of any potential toxic contaminants.
Dermatologic ...Topically, dandelion can cause contact dermatitis and erythema multiforme in sensitive individuals. Dandelion can cause an allergic reaction in individuals sensitive to the Asteraceae/Compositae family (13478,13481,42893,46945,46977). Members of this family include ragweed, chrysanthemums, marigolds, daisies, and many other herbs.
Endocrine ...In one report, a 56-year-old man with renal impairment developed hyperoxalaemia and peripheral gangrene after ingesting large amounts of dandelion tea (10 to 15 cups daily for 6 months). The adverse effect was attributed to the high oxalate content of dandelion tea (258 mcmol/L) and reduced renal oxalate clearance caused by renal impairment (90639). In another report, a 58-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes who was being treated with insulin developed hypoglycemic symptoms 2 weeks after beginning to eat salads containing dandelion (46960). The hypoglycemic effect was attributed to the potential alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity of dandelion.
Gastrointestinal ...Gastrointestinal symptoms, including stomach discomfort, diarrhea, and heartburn, have been reported following oral use of dandelion (19146,36931). A case of intestinal blockage has been reported for a patient who ingested a large amount of dandelion greens three weeks after undergoing a stomach operation (46981). Also, a case of hemorrhagic cystitis has been reported for a 33-year-old woman who took a specific herbal product (Slim-Kombu, Balestra and Mech, Vicenza, Italy) containing 20 herbal extracts, including dandelion extract. Symptoms resolved after the patient discontinued using the product, and symptoms resumed when the patient began taking the supplement again four months later. While various ingredients in the supplement may have contributed to the symptoms, it is possible that dandelion extract may have contributed to the effect due to its diuretic, laxative, cholagogue, and antirheumatic properties (46959).
Other ...Orally, products containing dandelion pollen can cause allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis (13479,13480). Also, rhinoconjunctivitis and asthma have been reported after handling products such as bird feed containing dandelion and other herbs, with reported positive skin tests for dandelion hypersensitivity (46948). Dandelion pollen may cause pollinosis, such as allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis (18065,46951,46964,46966,46972).
General ...European barberry is generally well tolerated when consumed in amounts commonly found in food. A thorough evaluation of safety outcomes has not been conducted for the use of larger, medicinal amounts. Topically, European barberry seems to be well tolerated.
Hepatic ...Orally, a case of hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia is reported in an adult male after consuming European barberry 15 drops and nannari root 15 drops twice a day for 2 weeks. The patient presented with lethargy, loss of appetite, and jaundice that progressed to high-grade fevers, chills, rigors, severe pancytopenia, and abnormal liver function tests. Liver biopsy was suggestive of drug-induced liver injury. The patient was hospitalized for multiple infections and symptomatic thrombocytopenia. Despite receiving supportive care, blood transfusions, and corticosteroids, the patient died 7 weeks after diagnosis (110021). The exact reason for this adverse effect is not clear.
General
...When used orally, Fucus vesiculosus may be unsafe due to its iodine content.
Topically, Fucus vesiculosus appears to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Goiter, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Thyroid cancer.
Cardiovascular ...In one report, a young adult with obesity developed palpitations and syncope after taking an oral weight loss supplement containing a combination of Fucus vesiculosus, dandelion, and boldo for 3 weeks. The patient was found to have a prolonged QT interval on ECG and frequent episodes of sustained polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (14321). It is not clear whether Fucus vesiculosus, another ingredient, or the combination of ingredients is responsible for this adverse effect. The product was not analyzed to determine the presence of any potential toxic contaminants.
Endocrine
...Orally, Fucus vesiculosus can cause or exacerbate hyperthyroidism due to its high iodine content (12789,13061,74217).
One case of hyperthyroidism has been reported for a 60-year-old patient taking lithium for bipolar disorder and a combination product containing Fucus vesiculosus 0.125 grams, cascara 0.170 grams, and Frangula 0.222 grams per tablet for laxative purposes. The patient had been taking one tablet of the combination laxative product daily for several years. Following discontinuation of the supplement, thyroid levels normalized (74217). Similar cases of hyperthyroidism have been reported for patients taking other seaweed-containing herbal supplements (Dream Shape; Ever Youth). Analyses of these supplements shows that these products contain triiodothyronine 1 mcg and thyroxine 3-4 mcg. In addition to seaweed, Dream Shape also contains hydrangea vine, maltose, chrysanthemum, Chinese matrimony vine, and sucrose, while Ever Youth contains radish, lotus leaf, chrysanthemum, hawthorn, senna tea, and Chinese matrimony vine (13061).
Orally, prolonged use of Fucus vesiculosus has been associated with hypothyroidism (13664). The iodine in Fucus vesiculosus can cause idiosyncratic reactions.
According to the Institute of Medicine Food and Nutrition Board, prolonged, high dietary intake of iodine is associated with goiter and an increased risk of thyroid cancer (7135).
Genitourinary ...A case of hemorrhagic cystitis characterized by dysuria and polyuria has been reported in a young adult who took a specific product (Slim-Kombu, Balestra and Mech) containing Fucus vesiculosus and 19 other herbal extracts orally for weight loss. Upon discontinuation, symptoms improved (46959). It is unclear if this effect was due to Fucus vesiculosus or other ingredients in the supplement.
Renal ...A case of hemorrhagic cystitis characterized by dysuria and polyuria has been reported in a young adult who took a specific product (Slim-Kombu, Balestra and Mech) containing Fucus vesiculosus and 19 other herbal extracts orally for weight loss. Upon discontinuation, symptoms improved (46959). It is unclear if this effect was due to Fucus vesiculosus or other ingredients in the supplement. Nephrotoxicity has been associated with oral intake of Fucus vesiculosus that was contaminated with arsenic (12800).
General
...Orally and topically, juniper seems to be generally well tolerated when used short-term in low doses.
However, a thorough evaluation of safety outcomes has not been conducted.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Topically: Allergies, skin irritation.
Dermatologic ...Topically, juniper can cause skin irritation. Signs of topical poisoning include burning, erythema, inflammation with blisters, and edema (4). Repeated exposure to the juniper pollen can cause occupational allergies that affect the skin (6). In a case report, a 62-year-old woman developed burn-like blistering lesions after carrying juniper in close contact to her skin. Concurrent sun exposure was thought to worsen the skin irritation caused by juniper (103756).
Genitourinary ...Orally, large amounts of the juniper berry can cause purplish urine (4).
Pulmonary/Respiratory ...Repeated exposure to the juniper pollen can cause occupational allergies that affect the respiratory tract (6).
General
...Orally, parsley seems to be well tolerated when used low to moderate doses.
Large doses may be unsafe.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally, Hallucinations, hemolytic anemia, hypotension, hepatic impairment, kidney impairment, nephrotic syndrome, paralysis, and thrombocytopenia purpura when taken in very high doses (200 grams parsley oil or 10 grams or more of parsley's apiole or myristicin constituents).
Cardiovascular ...Parsley contains the potentially toxic constituent, myristicin, which can cause significant adverse effects at high doses (11). Adverse effects specifically associated with myristicin include hypotension and bradycardia (4).
Dermatologic
...Orally, parsley oil can cause contact photodermatitis with sun exposure (4).
Topically, parsley can cause contact photodermatitis (4).
Hematologic ...Parsley contains the potentially toxic constituent apiole, which can cause significant adverse effects at high doses (11). Adverse effects specifically associated with more than 10 grams of the constituent apiole include hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia purpura (4).
Hepatic ...Parsley contains the potentially toxic constituents, apiole and myristicin, which can cause significant adverse effects at high doses (11). Adverse effects specifically associated with more than 10 grams of the constituent apiole include hepatic dysfunction (4). Adverse effects specifically associated with the constituent myristicin include fatty degeneration of the liver (4).
Immunologic ...A case of anaphylaxis involving severe angioedema leading to unconsciousness has been reported in a woman who consumed parsley 45 minutes prior to symptoms. The patient responded to epinephrine, antihistamines, intravenous fluids, oxygen therapy, and 1 mg/kg methylprednisolone. The woman had consumed one cup of chopped parsley nearly every day for several years, but upon skin testing, the patient tested positive to parsley (92869). There is also a report of lip angioedema after consumption of raw parsley. The patient had anaphylaxis to raw arugula, and reported itchy red lesions after contact with the leaves of either raw parsley or arugula. The patient had positive skin prick tests to both plants. The reaction may have been due to oral allergy syndrome, as the patient could tolerate cooked arugula and parsley, but not raw (92870).
Ocular/Otic ...Parsley contains the potentially toxic constituent, myristicin, which can cause significant adverse effects at high doses (11). An adverse effect specifically associated with the constituent myristicin includes deafness (4).
Psychiatric ...Parsley contains the potentially toxic constituent, myristicin, which can cause significant adverse effects at high doses (11). Adverse effects specifically associated with the constituent myristicin include giddiness and hallucinations (4).
Renal ...Parsley contains the potentially toxic constituents, apiole and myristicin, which can cause significant adverse effects at high doses (11). Adverse effects specifically associated with more than 10 grams of the constituent apiole include nephrosis and kidney irritation (4). Adverse effects specifically associated with the constituent myristicin include fatty degeneration of the kidneys (4).
General
...Uva ursi is generally well tolerated in low doses, short-term.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Diarrhea, nausea, stomach upset, and vomiting.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: At high doses (20 grams of dried herb), uva ursi has been reported to cause collapse, convulsions, cyanosis, delirium, shortness of breath, and tinnitus. Very high doses of 30 grams or more may be fatal.
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, uva ursi may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach upset (92148). It can also irritate the gastrointestinal tract (19).
Genitourinary ...Orally, uva ursi may cause the urine to be greenish-brown. It may also cause irritation and inflammation of the urinary tract mucous membranes (18).
Hepatic ...Uva ursi may be hepatotoxic. Theoretically, chronic use, especially in children, can cause liver impairment due its hydroquinone and high tannin content (4,18).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, around 20 grams of uva ursi is reported to supply up to one gram of hydroquinone, which can theoretically cause convulsions and delirium (4).
Ocular/Otic
...Orally, uva ursi may potentially cause retinal toxicity due to its hydroquinone content, which reduces melanin synthesis.
A 56-year-old female developed bilateral bull's-eye maculopathy, paracentral scotomas, and retinal thinning after 3 years of uva ursi tea ingestion (16900).
Taking around 20 grams of uva ursi orally is reported to supply up to one gram of hydroquinone, which can theoretically cause tinnitus (4).
Pulmonary/Respiratory ...Orally, around 20 grams of uva ursi is reported to supply up to one gram of hydroquinone, which can theoretically cause shortness of breath and cyanosis (4).
General
...Orally, yellow dock seems to be well tolerated when properly prepared and consumed in food amounts.
Consuming raw yellow dock leaves or rhizomes may be unsafe.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Raw leaves or rhizomes can cause hypocalcemia, kidney stones, and vomiting.
Cardiovascular ...Orally, yellow dock has been linked to ventricular fibrillation and death after ingestion of 500 grams (17). Oxalic acid, a constituent of yellow dock, reacts with calcium in plasma, forming insoluble calcium oxalate, which can cause hypocalcemia; the crystals may precipitate in the blood vessels and heart (12). Older or uncooked leaves should be avoided (6).
Dermatologic ...Orally, yellow dock can cause dermatitis when consumed in large amounts (4). Topically, contact with the plant may cause dermatitis in people sensitive to yellow dock (6).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, vomiting may occur after ingestion of fresh rhizome (18). Consuming excessive amounts can cause diarrhea and nausea (6). Excessive use can also cause abdominal cramps and intestinal atrophy (4). There is one report of a death, preceded by vomiting and diarrhea, after ingestion of 500 grams of yellow dock (17). Older or uncooked leaves should be avoided (6).
Genitourinary ...Orally, yellow dock can cause polyuria when consumed in large amounts (6).
Hematologic ...Orally, in one case report, a 38-year-old female developed immune-mediated thrombocytopenia after consuming a "cleansing" tea containing unknown amounts of yellow dock and burdock. The patient presented with bruising, mild weakness, and fatigue, which started 2-3 days after consuming the tea, and was found to have a platelet count of 5,000 per mcL. Symptoms resolved after platelet transfusion and treatment with oral dexamethasone (108971). It is unclear if these effects were caused by yellow dock, burdock, the combination, or other contributing factors.
Hepatic ...Orally, yellow dock has been linked to liver failure and death after ingestion of 500 grams (17). Oxalic acid, a constituent of yellow dock, reacts with calcium in plasma, forming insoluble calcium oxalate, which can cause hypocalcemia; the crystals may precipitate in the liver (12). Older or uncooked leaves should be avoided (6).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, yellow dock has been linked to coma and death after ingestion of 500 grams (17). Older or uncooked leaves should be avoided (6).
Pulmonary/Respiratory ...Orally, yellow dock has been linked to respiratory depression and death after ingestion of 500 grams (17). Oxalic acid, a constituent of yellow dock, reacts with calcium in plasma, forming insoluble calcium oxalate, which can cause hypocalcemia; the crystals may precipitate in the lungs (12). Older or uncooked leaves should be avoided (6).
Renal ...Orally, yellow dock can cause polyuria when consumed in large amounts (6). There is one report of a death, preceded by kidney failure, after ingestion of 500 grams (17). Oxalic acid, a constituent of yellow dock, reacts with calcium in plasma, forming insoluble calcium oxalate, which can cause hypocalcemia; the crystals may precipitate in the kidneys. Individuals with a history of kidney stones should use yellow dock cautiously (12). Older or uncooked leaves should be avoided (6).
Other ...Orally, yellow dock can cause hypokalemia when taken in large amounts (4). There is one report of a death, preceded by severe metabolic acidosis, after ingestion of 500 grams of yellow dock (17). Oxalic acid, a constituent of yellow dock, reacts with calcium in plasma, forming insoluble calcium oxalate, which can cause hypocalcemia; the crystals may precipitate in the kidneys, blood vessels, heart, lungs, and liver (12). Older or uncooked leaves should be avoided (6).
