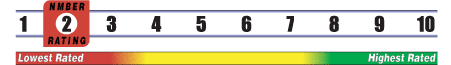
Each capsule contains: 3-(O-6-deoxy-alpha-l-mannopyranosyl-(1-6)-beta-d-glucopyranosyloxy)-2-(3,4- 50 mg • Chymotrypsin (7500 USP) 7.5 mg • Pancreatic Enzymes (25,000 FCC PU) 100 mg • Papain (960,000 FCC PU) 60 mg • Serrapeptase (12,000 SU) 19.8 mg • Bromelain stem (108 GDU) 45 mg • Trypsin (57,600 USP) 25 mg. Other Ingredients: Hypromellose, Inulin, Magnesium Stearate, Medium-Chain Triglycerides, Silicon Dioxide, Stearic Acid.
Brand name products often contain multiple ingredients. To read detailed information about each ingredient, click on the link for the individual ingredient shown above.

In 2004, Canada began regulating natural medicines as a category of products separate from foods or drugs. These products are officially recognized as "Natural Health Products." These products include vitamins, minerals, herbal preparations, homeopathic products, probiotics, fatty acids, amino acids, and other naturally derived supplements.
In order to be marketed in Canada, natural health products must be licensed. In order to be licensed in Canada, manufacturers must submit applications to Health Canada including information about uses, formulation, dosing, safety, and efficacy.
Products can be licensed based on several criteria. Some products are licensed based on historical or traditional uses. For example, if an herbal product has a history of traditional use, then that product may be acceptable for licensure. In this case, no reliable scientific evidence is required for approval.
For products with non-traditional uses, some level of scientific evidence may be required to support claimed uses. However, a high level of evidence is not necessarily required. Acceptable sources of evidence include at least one well-designed, randomized, controlled trial; well-designed, non-randomized trials; cohort and case control studies; or expert opinion reports.
Finished products licensed by Health Canada must be manufactured according to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) as outlined by Health Canada.
This product has been discontinued by the manufacturer.
This formula has been discontinued by the manufacturer and has been reformulated in 2014. The new formulation is still available under the same name.
This product contains glandular or organ material from animals. There have been concerns that animal materials might be obtained from diseased animals, including those harboring bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) or "mad cow disease." The risk of disease transmission appears to be low and there are no reports of BSE or other disease transmission to humans from dietary supplements containing animal material. Nonetheless, some people may want to avoid products containing animal material. Advise patients that this product is a source of animal glandular or organ material.
Below is general information about the effectiveness of the known ingredients contained in the product ProteoXyme. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
Below is general information about the safety of the known ingredients contained in the product ProteoXyme. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately. Doses up to 240 mg daily have been used safely for up to a year (6252,6253,10622,11457,18281,18284,91104,91105,91106,91111)(96449,103298). Higher doses up to 3200 mg daily have been used safely, short-term (18283,110546). ...when used topically and appropriately. Bromelain has been used safely as a debriding agent for up to 4 hours (18275,91113,103297,108148,108149,113899). Additionally, a retrospective cohort study in critically ill patients with severe burns suggests that use of bromelain as a debriding agent for up to 4 hours is not associated with a greater risk of bacteremia (113899).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used ophthalmically, as approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (9).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally in combination with trypsin for up to 10 days (716). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of chymotrypsin when administered by other routes.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods. Papain has Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status in the US (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately for medicinal purposes, short-term. Papain has been used in combination with other proteolytic enzymes at a dose of up to 1200 mg daily for up to 9 weeks (964,965,968,67831,67834). ...when used topically as a diluted solution in appropriate doses for up to 20 minutes (67835,67843,67845).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally in large amounts. In excessive doses, papain can cause significant side effects including esophageal perforation (6). ...when raw papain is used topically. Raw papain or papaya latex is a severe irritant and vesicant (6).
PREGNANCY: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally.
There is some concern that crude papain is teratogenic and embryotoxic (6).
LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately, short-term. Serrapeptase seems to be safe when used in clinical trials lasting up to 4 weeks (13151,13152,13153). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of serrapeptase when used long-term.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used topically by healthcare professionals trained in wound debridement (506). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of trypsin for its other uses. Although trypsin has been safely used in clinical research in doses of up to 288 mg orally daily in combination with other enzymes for up to 3 months, it is unclear if trypsin taken orally alone is safe (37193,92235,99473).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
Below is general information about the interactions of the known ingredients contained in the product ProteoXyme. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
Bromelain may have antiplatelet effects and may increase the risk of bleeding if used with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
There is one case report of a patient experiencing minor bruising while taking bromelain with naproxen (14806). Bromelain is thought to have antiplatelet activity (10639,14806,18285,18286,37234). Whether this interaction is of concern with topical bromelain is unclear. Interference with coagulation of burn wounds has been reported in a patient receiving bromelain-based enzymatic debridement. However, observational research has found that topical bromelain debridement is not associated with increases or decreases in laboratory markers of coagulation when compared with surgical debridement (110547).
|
Theoretically, bromelain might increase levels of tetracycline antibiotics.
Laboratory research suggests that bromelain might increase the absorption of tetracycline antibiotics. However, a study in healthy adults reported no difference in tetracycline plasma levels when a 500 mg dose was taken with or without bromelain 80 mg (14296).
|
Theoretically, papain might increase the effects and side effects of warfarin.
In one case report, a patient previously stable on warfarin was found to have an international normalization ratio (INR) of 7.4, which was attributed to ingestion of a supplement containing papain from papaya extract (613).
|
Theoretically, taking serrapeptase with drugs that have antiplatelet or anticoagulant effects might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
|
Below is general information about the adverse effects of the known ingredients contained in the product ProteoXyme. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
General
...Orally, bromelain seems to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Diarrhea, flatulence, gastric upset, headache.
Topically: Pruritus, urticaria.
Dermatologic
...Topically, bromelain may cause dermal allergic reactions including urticaria, pruritus, and skin swelling (9184).
Redness, swelling, burning, pain at the application site, and cellulitis have also been reported rarely (108148,113513). In one case, a fixed drug eruption with pruritis near the groin was reported in a 33-year-old male taking bromelain 50 mg orally daily for 10 days. After discontinuation of bromelain and treatment with topical corticosteroid, the lesion resolved. Upon re-challenge with bromelain, the lesion reappeared in the same area (103300).
In another case report, a 61-year-old male with a history of chronic lower leg ulceration secondary to chronic venous hypertension and recurrent deep vein thrombosis on rivaroxaban presented with a deep-dermal burn on his lower calf. Bromelain-based topical enzymatic debridement agent Nexobrid 2 grams was applied to the burn site. Thirty minutes later, the patient experienced two instances of hemorrhage at the site of debridement. The patient was stabilized and treated with fluids, packed red cells, and tranexamic acid, and then the Nexobrid was removed (111656). Caution should be used in patients with underlying coagulopathies.
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, bromelain may cause gastrointestinal disturbances, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, and abdominal pain (9184,18274,18282,96216,113513).
Immunologic
...Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated allergic reactions to bromelain may occur (9184).
If inhaled, bromelain may cause sensitization and allergic reactions such as asthma (37199,37215,37233). In case reports of occupational inhalation of bromelain, additional allergic symptoms included difficulty swallowing, throat itching, eye irritation, and rhinitis (37214).
General ...There is currently a limited amount of information available about the adverse effects of chymotrypsin. Orally, hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported (9). When injected into the eye, chymotrypsin has been reported to cause increased intraocular pressure and uveitis (9,509).
Immunologic ...Rarely, chymotrypsin has been reported to cause anaphylactic reactions characterized by dyspnea, urticaria, edema, shock, vascular collapse, and unconsciousness, which can lead to death (9,509).
Ocular/Otic ...Intraocular injections of chymotrypsin have been reported to cause increased intraocular pressure, corneal edema, striation, uveitis, iridoplegia, and filamentary keratitis (9,509).
General
...Orally and topically, papain seems to be well tolerated when used short-term at appropriate doses.
Taking high oral doses may be unsafe.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Topically: Urticaria and pruritus in sensitive individuals.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Esophageal perforation and severe gastritis with high doses.
Dermatologic ...Topically, papain can cause itching (966). Urticarial reactions and itching have been reported in people occupationally exposed to papain, with papain confirmed as the causative agent by skin prick tests or radioallergosorbent tests (RAST) (95533,95534). In a randomized controlled trial assessing the effects of papain, trypsin, and chymotrypsin on adverse effects from radiotherapy, moderate to severe epitheliolysis was more frequent in the enzyme-treated group than the placebo group (67834). It is unclear if this adverse effect is due to papain, other enzymes, or the combination.
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, papain has been associated with diarrhea. In a randomized controlled trial assessing the effects of papain, trypsin, and chymotrypsin on adverse effects from radiotherapy, moderate to severe diarrhea was more frequent in the enzyme-treated group than the placebo group (67834). However, it is unclear if this adverse effect is due to papain, other enzymes, or the combination. Papain has also been associated with gastric ulcers and esophageal perforation in case reports of phytobezoars treated with papain (67848). In general, large amounts of papain can cause esophageal perforation (6). Ingestion of papaya latex (raw papain) can cause severe gastritis.
Genitourinary ...Orally, papain has been associated with hypernatremia in case reports of phytobezoars treated with papain (67848).
Immunologic ...Orally, papain may cause allergic reactions, including itchy watery eyes, runny nose, sneezing, abdominal cramps, sweating, and diarrhea, in individuals sensitive to papain (6,967). Occupational exposure to airborne papain dust may also cause respiratory allergic reactions (95532,95533,95534,95535,95536).
Pulmonary/Respiratory ...Occupational exposure to airborne papain dust may cause respiratory allergic reactions. Symptoms include rhinitis, sneezing, conjunctivitis, dyspnea, wheezing, cough, and asthma. In most cases, papain is confirmed as the causative agent by skin prick tests, radioallergosorbent tests (RAST), or detection of papain-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) and IgG (95532,95533,95534,95535,95536).
General
...Orally, serrapeptase seems to be well-tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Epigastric pain, gastrointestinal upset, nausea.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Bullous pemphigoid
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, some patients have reported experiencing epigastric pain, gastrointestinal upset, and nausea; however, these side effects appear to occur at the same rate as placebo (13152).
Immunologic ...There is a case report of bullous pemphigoid, an autoimmune subepidermal dermatosis, in an elderly man who took serrapeptase (13154).
General ...Topically, trypsin can cause localized pain and transient burning (506). Orally, trypsin taken in combination with other enzymes can cause mild-to-moderate gastrointestinal symptom such as nausea, heartburn, and stomach pain (37193,92235). It is not known if trypsin or other enzymes causes these adverse effects.
Dermatologic ...Topically, trypsin can cause localized pain and transient burning (506).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, trypsin taken in combination with other enzymes can cause mild-to-moderate gastrointestinal symptom such as nausea, heartburn, and stomach pain (37193,92235). It is not known if trypsin or other enzymes causes these adverse effects.
