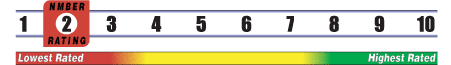
| Ingredients | Amount Per Serving |
|---|---|
|
Calories
|
14 Calorie(s) |
|
Total Fat
|
0 mg |
|
Cholesterol
|
0 mg |
|
(Na)
|
14 mg |
|
Total Carbohydrates
|
3 Gram(s) |
|
Protein
|
0.5 Gram(s) |
|
Natural Energy, Endurance, and Focus
|
1811 mg |
|
(Panax ginseng )
(root)
|
|
|
(seed)
|
|
|
(root)
|
|
|
Natural Vascularity
|
1695 mg |
|
(root)
|
|
|
(juice)
|
|
|
(fruit)
|
|
|
(bark)
|
|
|
(leaf & flower)
|
|
|
(seed)
|
|
|
(fruit)
|
|
|
Natural Fat Utilization
|
287.5 mg |
|
(leaf)
|
|
|
(bark)
|
|
|
(fruit)
|
|
|
Natural Sweetening
|
140 mg |
|
(Stevia )
(leaf)
|
None
Below is general information about the effectiveness of the known ingredients contained in the product RAW Tea. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
Below is general information about the safety of the known ingredients contained in the product RAW Tea. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately, short-term. Bee pollen has been safely used in clinical trials lasting up to 30 days (7062,7063,12008,33973). There is also preliminary evidence that taking 2 tablets twice daily of a specific combination product containing royal jelly 6 mg, bee pollen extract 36 mg, and bee pollen plus pistil extract 120 mg (Femal, Natumin Pharma) per tablet for up to 2 months seems to be safe (12008).
PREGNANCY: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally.
There is some concern that bee pollen might have uterine stimulant effects (5,6,11); avoid using.
LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used in amounts commonly found in foods.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately for medicinal purposes, short term. Beetroot juice has been safely used in clinical trials in doses of up to 500 mL daily for up to 7 days and a beetroot-based nutritional gel has been used safely in doses of up to 100 grams daily for 8 days (94461,94462,94464,100149,100152,100153).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of beets used medicinally during pregnancy and breast-feeding.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately in amounts commonly found in foods. Bilberry has Generally Recognized As Safe status (GRAS) for use in foods in the US (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately for medicinal purposes. Bilberry fruit extracts have been used with apparent safety in clinical trials at a dose of up to 160 mg daily for up to 6 months (39,40,8139,9739,14280,35472,35510,35512,103190,104192,104195). A higher bilberry extract dose of 1.4 grams daily has been used with apparent safety for up to 4 weeks (104194). Whole bilberries or bilberry juice have also been consumed with apparent safety in quantities of 100-160 grams daily for up to 35 days (35463,91506).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when the leaves are used orally in high doses or for a prolonged period. Death can occur with chronic use of 1.5 gram/kg daily (2).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: LIKELY SAFE
when used orally in the amounts commonly found in foods.
However, there is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of bilberry when used in medicinal amounts during pregnancy and lactation; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods. Bitter orange has Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status in the US (4912,35751).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when bitter orange essential oil is used topically or by inhalation as aromatherapy (6972,7107,98331,104186,104187,108642).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally for medicinal purposes. Although single doses of synephrine, or low daily doses used short-term, may be safe in healthy adults (2040,11269,15381,35757,35759,91681,97256,98332), laboratory analyses raise concerns that many marketed bitter orange products contain higher amounts of synephrine and other natural and synthetic amines than on the label, increasing the risk for serious stimulant-related adverse effects (104185). Additionally, there is a lack of agreement regarding a safe daily dose of synephrine. Health Canada has approved 50 mg of p-synephrine daily when used alone, or 40 mg of p-synephrine in combination with up to 320 mg of caffeine daily in healthy adults (91684). The Federal Institute for Risk Assessment in Germany recommends that supplements should provide no more than 6.7 mg of synephrine daily. This recommendation is meant to ensure that patients who frequently consume synephrine in conventional foods will receive no more than 25.7 mg daily (91290). These limits are intended to reduce the risk for serious adverse effects. There have been several case reports of ischemic stroke and cardiotoxicity including tachyarrhythmia, cardiac arrest, syncope, angina, myocardial infarction, ventricular arrhythmia, and death in otherwise healthy patients who have taken bitter orange extract alone or in combination with other stimulants such as caffeine (2040,6979,12030,13039,13067,14326,14342,91680).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: LIKELY SAFE
when used orally in the amounts found in foods.
Bitter orange has Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status in the US (4912).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally for medicinal purposes.
There are case reports of cardiotoxicity including tachyarrhythmia, syncope, and myocardial infarction in otherwise healthy adults who have taken bitter orange extract alone or in combination with other stimulants such as caffeine (2040,6979,12030,13039,13067,14326,14342,91680). The effects of bitter orange during lactation are unknown; avoid use.
LIKELY SAFE ...when consumed in amounts commonly found in foods. Ceylon cinnamon has Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) status in the US for use as a spice or flavoring agent (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately in medicinal amounts. Ceylon cinnamon 0.5-3 grams daily has been safely used in studies lasting up to 6 months (4,12,97248,97250,99874). ...when used as a mouth rinse for up to 15 days (92071). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of Ceylon cinnamon when used orally in greater amounts or for longer periods. Ceylon cinnamon contains trace amounts of coumarin (108260). In very high doses, coumarin can cause hepatotoxicity (15302). However, since the amount of coumarin in Ceylon cinnamon is negligible, it is unlikely to cause toxic effects (89652,92072,92073).
PREGNANCY: LIKELY SAFE
when consumed in amounts commonly found in foods (4912).
PREGNANCY: LIKELY UNSAFE
when used orally in amounts greater than those found in foods.
Fetal abnormalities have been reported in animals (4,12).
LACTATION: LIKELY SAFE
when consumed in amounts commonly found in foods (4912).
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of Ceylon cinnamon in amounts greater than those found in foods.
LIKELY SAFE . .when used orally and appropriately. Cranberry juice up to 300 mL daily and cranberry extracts in doses up to 800 mg twice daily have been safely used in clinical trials (3333,3334,6758,6760,7008,8252,8253,8254,8995,11328) (16415,16720,17100,17126,17176,17210,17524,46379,46388,46389)(46390,46425,46439,46443,46465,46456,46466,46467,46469,46471)(46496,46499,90044,102847,111407).
CHILDREN: LIKELY SAFE
when cranberry juice is consumed in amounts commonly found in the diet (2811,6759,46441,46452,46470,111407).
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of cranberry when used in medicinal amounts in children.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: LIKELY SAFE
when consumed in amounts commonly found in the diet.
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of cranberry when used therapeutically during pregnancy or lactation; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally in the amounts typically found in foods. Elderberry has generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status in the US (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when elderberry fruit extract is used orally, short-term. One specific elderberry fruit extract (Sambucol, Nature's Way) has been used with apparent safety for up to 5 days (5260,12235,103831); another (BerryPharma, Iprona AG) has been used with apparent safety for up to 15 days (91374). A specific elderberry fruit extract lozenge (ViraBLOC, HerbalScience) has been used with apparent safety for 2 days (17022). Other elderberry fruit extracts have been used with apparent safety for up to 12 weeks (21141,21142).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when elder tree leaves and stems, or unripe or uncooked elderberries, are consumed. The unripe green fruit, as well as the leaves and stems of the elder tree, contain a cyanide-producing chemical, which can cause serious toxicity (17020,17021,21143,21144,91374). Cooking eliminates the toxin.
CHILDREN: LIKELY SAFE
when consumed in the amounts typically found in foods.
CHILDREN: POSSIBLY SAFE
when used orally for up to 3 days.
A specific fruit extract (Sambucol, Nature's Way) has been used in doses of 15 mL twice daily for 3 days in children 5 years and older (5260,103831).
CHILDREN: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when unripe or uncooked elderberries are consumed.
The unripe green fruit, as well as the leaves and stems of the elder tree, contain a cyanide-producing chemical , which can cause serious toxicity (17020,17021,21143,21144,91374). Cooking eliminates the toxin.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: LIKELY SAFE
when consumed in the amounts typically found in foods.
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of elderberry when used for medicinal purposes; avoid using in amounts greater than those found in foods.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods. Grapes and grape skin extracts have Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) status for use in foods in the US (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when the whole fruit of the grape, or extracts of the fruit, seed, or leaf, are used orally and appropriately in medicinal amounts. Grape seed extracts have been used with apparent safety in doses up to 200 mg daily for up to 11 months (9182,53016) and in doses up to 2000 mg daily for up to 3 months (53149,53190). Specific grape fruit extracts (Stilvid, Actafarma; Cognigrape, Bionap srl) have been used with apparent safety in doses up to 250-350 mg daily for 3-12 months or 700 mg daily for 6 months (53254,53256,96198). A specific grape leaf extract (AS 195, Antistax, Boehringer Ingelheim) has been used with apparent safety in doses up to 720 mg daily for up to 3 months (2538,52985,53005,53206). A preparation of dehydrated whole grapes, equivalent to 250 grams of fresh grapes daily, has also been used with apparent safety for up to 30 days (18228). A specific grape seed extract (Enovita; Indena SpA) 150 mg twice daily, standardized to provide at least 95% oligomeric proanthocyanins, has been used with apparent safety for up to 16 weeks (108091) ...when used topically and appropriately. Creams and ointments containing grape seed extract 2% or 5% have been used topically with apparent safety for up to 3 weeks (91539,100955). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of other grape plant parts when used topically.
CHILDREN: LIKELY SAFE
when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods.
Grapes and grape skin extracts have Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) status for use in foods in the US (4912). However, whole grapes should be eaten with caution in children aged 5 years and under. Whole grapes can be a choking hazard for young children (96193). To reduce the risk of choking, whole grapes should be cut in half or quartered before being given to children. There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of grape when used in medicinal amounts in children.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: LIKELY SAFE
when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods.
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of medicinal amounts during pregnancy and breast-feeding; avoid using in amounts greater than what is commonly found in foods.
LIKELY SAFE ...when green tea is consumed as a beverage in moderate amounts (733,6031,9222,9223,9225,9226,9227,9228,14136,90156)(90159,90168,90174,90184,95696). Green tea contains caffeine. According to a review by Health Canada, and a subsequent large meta-analysis conducted in the US, drinking up to 8 cups of green tea daily, or approximately 400 mg of caffeine, is not associated with significant adverse cardiovascular, bone, behavioral, or reproductive effects in healthy adults (11733,98806). The US Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee states that there is strong and consistent evidence that consumption of caffeine 400 mg daily is not associated with increased risk of major chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease or cancer, in healthy adults (98806). ...when green tea extract cream or ointment is used topically and appropriately, short-term. A green tea extract 3% cream, applied twice daily, has been used with apparent safety for up to 8 weeks, and a specific green tea extract ointment (Veregen, Bradley Pharmaceuticals) providing 15% kunecatechins has been safely used for up to 16 weeks (15067). The safety of treatment for longer durations or multiple treatment courses is not known.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when green tea extract is used orally. Green tea extract containing 7% to 12% caffeine has been used safely for up to 2 years (8117,37725). Also decaffeinated green tea extract up to 1.3 grams daily enriched in EGCG has been used safely for up to 12 months (90158,97131). In addition, green tea extract has been safely used as part of an herbal mixture also containing garcinia, coffee, and banaba extracts for 12 weeks (90137). ...when used topically and appropriately as a cream or mouthwash (6065,11310,90141,90150,90151).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when consumed as a beverage in large quantities. Green tea contains a significant amount of caffeine. Chronic use, especially in large amounts, can produce tolerance, habituation, psychological dependence, and other significant adverse effects. Doses of caffeine greater than 600 mg per day, or approximately 12 cups of green tea, have been associated with significant adverse effects such as tachyarrhythmias and sleep disturbances (11832). These effects would not be expected to occur with the consumption of decaffeinated green tea. Keep in mind that only the amount of ADDED caffeine must be stated on product labels. The amount of caffeine found in ingredients such as green tea, which naturally contains caffeine, does not need to be provided. This can make it difficult to determine the total amount of caffeine in a given product. There is also some speculation that green tea products containing higher amounts of the catechin epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) might have increased risk of adverse events. Some research has found that taking green tea products containing EGCG levels greater than 200 mg is associated with increased risk of mild adverse effects such as constipation, increased blood pressure, and rash (90161). Other research has found that doses of EGCG equal to or above 800 mg daily may be associated with increased risk of liver injury in humans (95440,95696,97131).
LIKELY UNSAFE ...when used orally in very high doses. The fatal acute oral dose of caffeine is estimated to be 10-14 grams (150-200 mg per kilogram). Serious toxicity can occur at lower doses depending on variables in caffeine sensitivity such as smoking, age, and prior caffeine use (11832).
CHILDREN: POSSIBLY SAFE
when used orally by children and adolescents in amounts commonly found in foods and beverages (4912,11833).
Intake of caffeine in doses of less than 2.5 mg/kg daily is not associated with significant adverse effects in children and adolescents (11733,98806). ...when used for gargling three times daily for up to 90 days (90150).
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of green tea extract when used orally in children. However, taking green tea extract orally has been associated with potentially serious, albeit uncommon and unpredictable cases, of hepatotoxicity in adults. Therefore, some experts recommend that children under the age of 18 years of age do not use products containing green tea extract (94897).
PREGNANCY: POSSIBLY SAFE
when used orally in moderate amounts.
Due to the caffeine content of green tea, pregnant patients should closely monitor their intake to ensure moderate consumption. Fetal blood concentrations of caffeine approximate maternal concentrations (4260). The use of caffeine during pregnancy is controversial; however, moderate consumption has not been associated with clinically important adverse fetal effects (2708,2709,2710,2711,9606,11733,16014,16015,98806). In some studies consuming amounts over 200 mg daily is associated with a significantly increased risk of miscarriage (16014). This increased risk may be most likely to occur in those with genotypes that confer a slow rate of caffeine metabolism (98806). According to a review by Health Canada, and a subsequent large meta-analysis conducted in the US, most healthy pregnant patients can safely consume doses up to 300 mg daily without an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, preterm birth, fetal growth retardation, or congenital malformations (11733,98806). Advise keeping caffeine consumption below 300 mg daily. This is similar to the amount of caffeine in about 6 cups of green tea. Keep in mind that only the amount of ADDED caffeine must be stated on product labels. The amount of caffeine found in ingredients such as green tea, which naturally contains caffeine, does not need to be provided. This can make it difficult to determine the total amount of caffeine in a given product. Based on animal models, green tea extract catechins are also transferred to the fetus, but in amounts 50-100 times less than maternal concentrations (15010). The potential impact of these catechins on the human fetus is not known, but animal models suggest that the catechins are not teratogenic (15011).
PREGNANCY: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally in amounts providing more than 300 mg caffeine daily.
Caffeine from green tea crosses the placenta, producing fetal blood concentrations similar to maternal levels (4260). Consumption of caffeine in amounts over 300 mg daily is associated with a significantly increased risk of miscarriage in some studies (16014,98806). Advise keeping caffeine consumption from all sources below 300 mg daily. This is similar to the amount of caffeine in about 6 cups of green tea. High maternal doses of caffeine throughout pregnancy have also resulted in symptoms of caffeine withdrawal in newborn infants (9891). High doses of caffeine have also been associated with spontaneous abortion, premature delivery, and low birth weight (2709,2711). However, some research has also found that intrauterine exposure to even modest amounts of caffeine, based on maternal blood levels during the first trimester, is associated with a shorter stature in children ages 4-8 years (109846). Keep in mind that only the amount of ADDED caffeine must be stated on product labels. The amount of caffeine found in ingredients such as green tea, which naturally contains caffeine, does not need to be provided. This can make it difficult to determine the total amount of caffeine in a given product.
There is also concern that consuming large amounts of green tea might have antifolate activity and potentially increase the risk of folic acid deficiency-related birth defects. Catechins in green tea inhibit the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase in vitro (15012). This enzyme is responsible for converting folic acid to its active form. Preliminary evidence suggests that increasing maternal green tea consumption is associated with increased risk of spina bifida (15068). Also, evidence from epidemiological research suggests that serum folate levels in pregnant patients with high green tea intake (57.3 mL per 1000 kcal) are decreased compared to participants who consume moderate or low amounts of green tea (90171). More evidence is needed to determine the safety of using green tea during pregnancy. For now, advise pregnant patients to avoid consuming large quantities of green tea.
LACTATION: POSSIBLY SAFE
when used orally in moderate amounts.
Due to the caffeine content of green tea, nursing parents should closely monitor caffeine intake. Breast milk concentrations of caffeine are thought to be approximately 50% of maternal serum concentrations (9892).
LACTATION: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally in large amounts.
Consumption of green tea might cause irritability and increased bowel activity in nursing infants (6026). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of green tea extracts when applied topically during breast-feeding.
LIKELY SAFE ...when consumed in amounts typically found in foods. Guarana has Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status for use in foods in the US (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately, short-term (12). Guarana contains caffeine. According to a review by Health Canada, and a subsequent large meta-analysis conducted in the US, doses of caffeine up to 400 mg daily are not associated with significant adverse cardiovascular, bone, behavioral, or reproductive effects in healthy adults (11733,98806). The US Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee states that there is strong and consistent evidence that consumption of caffeine 400 mg daily is not associated with increased risk of major chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease or cancer, in healthy adults (98806).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally long-term or in high doses. Guarana contains a significant amount of caffeine. Chronic use, especially in large amounts, can produce tolerance, habituation, psychological dependence, and other significant adverse effects. Acute use of high doses, typically above 400 mg per day, has been associated with significant adverse effects such as tachyarrhythmias and sleep disturbances (11832,95503,98806). These effects would not be expected to occur with the consumption of decaffeinated guarana.
LIKELY UNSAFE ...when used orally in very high doses. The fatal acute oral dose of caffeine is estimated to be 10-14 grams (150-200 mg per kilogram). Serious toxicity can occur at lower doses depending on variables in caffeine sensitivity such as smoking, age, or prior caffeine use (11832,54425).
PREGNANCY: POSSIBLY SAFE
when consumed in amounts commonly found in foods.
Due to the caffeine content of guarana, intake should be closely monitored during pregnancy to ensure moderate consumption. Although it is not considered a teratogen, caffeine crosses the placenta and causes dose-dependent increases in fetal blood concentrations (4260). The use of caffeine during pregnancy is controversial; however, moderate consumption has not been associated with clinically important adverse fetal effects (2708,2709,2710,2711,9606,11733,16014,16015,98806). In some studies, consuming amounts over 200 mg daily is associated with a significantly increased risk of miscarriage (16014). This increased risk may be most likely to occur in individuals with genotypes that confer a slow rate of caffeine metabolism (98806). According to a review by Health Canada, and a subsequent large meta-analysis conducted in the US, caffeine can be safely consumed in doses up to 300 mg daily without an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, preterm birth, fetal growth retardation, or congenital malformations (11733,98806). However, some research has also found that intrauterine exposure to even modest amounts of caffeine, based on maternal blood levels during the first trimester, is associated with a shorter stature in children ages 4-8 years (109846). Advise individuals to keep caffeine consumption below 300 mg daily during pregnancy.
PREGNANCY: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally in amounts over 300 mg daily.
Although it is not considered a teratogen, caffeine crosses the placenta and causes dose-dependent increases in fetal blood concentrations (4260,98806). Consumption of caffeine in amounts over 300 mg daily is associated with a significantly increased risk of miscarriage in some studies (16014,98806). Advise keeping caffeine consumption from all sources below 300 mg daily. High maternal doses of caffeine throughout pregnancy have resulted in symptoms of caffeine withdrawal in newborn infants (9891). High doses of caffeine have also been associated with spontaneous abortion, premature delivery, and low birth weight (2709,2711).
LACTATION: POSSIBLY SAFE
when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods.
Due to the caffeine content of guarana, intake should be closely monitored when breast-feeding. Breast milk concentrations of caffeine are thought to be approximately 50% of serum concentrations (9892).
LACTATION: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally in large amounts.
Consumption of guarana might cause irritability and increased bowel activity in nursing infants (6026). Large doses or excessive intake of guarana should be avoided when breast-feeding.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately, short-term. Hawthorn preparations in doses of up to 1800 mg daily seem to be safe when used for up to 16 weeks. Although hawthorn might be safe for long-term use, current studies have not evaluated safety past 16 weeks (8279,8280,8281,10144,17203,104689). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of hawthorn when used topically.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when maca is consumed in food amounts (9926).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately, short term. Maca appears to be safe in doses up to 3 grams daily for 4 months (9928,10218,18289,90278,108603).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately, short-term. Panax ginseng seems to be safe when used for up to 6 months (8813,8814,17736,89741,89743,89745,89746,89747,89748,103044)(103477,114980,114981,114984,114985). Panax ginseng sprout extract has also been used with apparent safety in doses up to 450 mg daily for up to 12 weeks (114983).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally, long-term. There is some concern about the long-term safety due to potential hormone-like effects, which might cause adverse effects with prolonged use (12537). Tell patients to limit continuous use to less than 6 months. There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of Panax ginseng when used topically.
CHILDREN: LIKELY UNSAFE
when used orally in infants.
Use of Panax ginseng in newborns is associated with intoxication that can lead to death (12). There is limited reliable information available about use in older children (24109,103049); avoid using.
PREGNANCY: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally.
Ginsenoside Rb1, an active constituent of Panax ginseng, has teratogenic effects in animal models (10447,24106,24107); avoid using.
LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately, short-term. Royal jelly 1-4.8 grams daily for up to 1 year has been used in clinical research without reported adverse effects (95869,95870,102527,102528,105773,105774)....when used topically and appropriately for up to 6 months (71980,102526).
CHILDREN: POSSIBLY SAFE
when used orally and appropriately for up to 6 months.
A specific royal jelly product (Bidro) 150 mg twice daily has been used with apparent safety for 3-6 months in children 5-16 years of age (71968).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately. Sodium is safe in amounts that do not exceed the Chronic Disease Risk Reduction (CDRR) intake level of 2.3 grams daily (100310). Higher doses can be safely used therapeutically with appropriate medical monitoring (26226,26227).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally in high doses. Tell patients to avoid exceeding the CDRR intake level of 2.3 grams daily (100310). Higher intake can cause hypertension and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (26229,98176,98177,98178,98181,98183,98184,100310,109395,109396,109398,109399). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of sodium when used topically.
CHILDREN: LIKELY SAFE
when used orally and appropriately (26229,100310).
Sodium is safe in amounts that do not exceed the CDRR intake level of 1.2 grams daily for children 1 to 3 years, 1.5 grams daily for children 4 to 8 years, 1.8 grams daily for children 9 to 13 years, and 2.3 grams daily for adolescents (100310).
CHILDREN: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally in high doses.
Tell patients to avoid prolonged use of doses exceeding the CDRR intake level of 1.2 grams daily for children 1 to 3 years, 1.5 grams daily for children 4 to 8 years, 1.8 grams daily for children 9 to 13 years, and 2.3 grams daily for adolescents (100310). Higher intake can cause hypertension (26229).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: LIKELY SAFE
when used orally and appropriately.
Sodium is safe in amounts that do not exceed the CDRR intake level of 2.3 grams daily (100310).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally in higher doses.
Higher intake can cause hypertension (100310). Also, both the highest and the lowest pre-pregnancy sodium quintile intakes are associated with an increased risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, including gestational hypertension and pre-eclampsia, and the delivery of small for gestational age (SGA) infants when compared to the middle intake quintile (106264).
LIKELY SAFE ...when certain stevia constituents, including stevioside and rebaudiosides A, D, and M, are used orally as sweeteners in foods. These constituents have generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status in the US for this purpose (16699,16700,16702,16705,16706,108049). The stevia constituent stevioside has been safely used in doses of up to 1500 mg daily for 2 years (11809,11810,11811,113006). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of whole stevia or stevia extracts when used orally. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has determined that the acceptable intake of steviol glycosides is 4 mg/kg daily (106456); however, it is unclear how this relates to the use of whole stevia or stevia extract.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally. Yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, has been associated with serious adverse effects including cardiac arrhythmia, agitation, myocardial infarction, seizure, and others (17465). Some research shows that yohimbine can be safely used under close medical supervision for up to 10 weeks (3305,3307,3311,3313). However, due to safety concerns, yohimbe should not be used without medical supervision.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally.
Yohimbe might have uterine relaxant effects and also cause fetal toxicity (19).
Below is general information about the interactions of the known ingredients contained in the product RAW Tea. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
There is some concern that bee pollen might interact with warfarin and increase the risk of bleeding.
In one case report, a patient on warfarin had a stable international normalized ratio (INR) of 1.9-3.3 for 9 months. The patient's INR was found to be 7.1 after starting bee pollen granules one teaspoon twice daily for approximately one month. The patient's warfarin dose was decreased by approximately 11% in order to return the INR to the therapeutic range while continuing the bee pollen supplement (18063).
|
Theoretically, beet might decrease the levels and clinical effects of CYP1A2 substrates.
In vitro research suggests that beet induces CYP1A2 enzymes (111404).
|
Theoretically, beet might increase the levels of CYP3A4 substrates.
In vitro research suggests that betanin, the major pigment in beet, competitively inhibits CYP3A4 in a dose-dependent manner similarly to strong CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole (113425).
|
Theoretically, bilberry fruit extract might increase the risk of bleeding when taken with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
|
Theoretically, bilberry leaf or fruit extract may increase the risk of hypoglycemia when taken with antidiabetes drugs.
Animal research suggests that bilberry leaf extract might have blood glucose-lowering activity (1264). Also, one small clinical trial in patients with type 2 diabetes shows that taking bilberry fruit extract 470 mg as a single dose prior to an oral glucose tolerance test lowers plasma glucose levels when compared with placebo (91507).
|
Theoretically, bilberry fruit extract might decrease levels of drugs metabolized by CYP2E1.
Animal research shows that exposure to small concentrations of bilberry extract in drinking water for around one month increased CYP2E1 activity by 31%. However, exposure over a 2-month period did not increase CYP2E1 activity (103191). This effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, bilberry fruit extract might reduce the efficacy of erlotinib.
In vitro research suggests that bilberry fruit extract and its constituents, delphinidin and delphinidin-3-O-glucoside, inhibit the activity of erlotinib (97031). This interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, bitter orange might increase the risk of hypoglycemia when taken with antidiabetes drugs.
Some clinical research shows that drinking a tea containing bitter orange and Indian snakeroot reduces fasting and postprandial glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes who are using antidiabetes drugs (35751). However, it is unclear if these effects are due to bitter orange, Indian snakeroot, or the combination. An animal study also shows that p-synephrine in combination with gliclazide , a sulfonylurea, causes an additional 20% to 44% decrease in glucose levels when compared with gliclazide alone (95658).
|
Bitter orange might increase blood pressure and heart rate when taken with caffeine.
|
Bitter orange might affect colchicine levels.
Colchicine is a substrate of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4). Bitter orange has been reported to inhibit CYP3A4 and increase levels of CYP3A4 substrates (7029,11362,93470). However, one small clinical study in healthy adults shows that drinking bitter orange juice 240 mL twice daily for 4 days and taking a single dose of colchicine 0.6 mg on the 4th day decreases colchicine peak serum levels by 24%, time to peak serum level by 1 hour, and overall exposure to colchicine by 20% (35762). The clinical significance of this finding is unclear.
|
Theoretically, bitter orange might increase levels of drug metabolized by CYP2D6.
In vitro research shows that octopamine, a constituent of bitter orange, weakly inhibits CYP2D6 enzymes (91878). This effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Bitter orange might increase levels of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4.
Small clinical studies suggest that single or multiple doses of freshly squeezed bitter orange juice 200-240 mL can inhibit CYP3A4 metabolism of drugs (7029,11362,93470), causing increased drug levels and potentially increasing the risk of adverse effects. However, the extent of the effect of bitter orange on CYP3A4-mediated drug interactions is unknown. Some evidence suggests that bitter orange selectively inhibits intestinal CYP3A4, but not hepatic CYP3A4. Its effect on P-glycoprotein, which strongly overlaps with CYP3A4 interactions, is unclear (7029,11269,11270,11362). One small clinical study shows that drinking 8 ounces of freshly squeezed bitter orange juice has no effect on cyclosporine, which seems to be more dependent on hepatic CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein than intestinal CYP3A4 (11270).
|
Bitter orange might increase blood levels of dextromethorphan.
One small clinical study shows that bitter orange juice increases dextromethorphan levels, likely through cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibition (11362). Theoretically, bitter orange might increase the risk for dextromethorphan-related adverse effects.
|
Bitter orange might increase blood levels of felodipine.
One small clinical study shows that bitter orange juice increases felodipine levels, likely through cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibition (7029). Theoretically, bitter orange might increase the risk for felodipine-related adverse effects.
|
Bitter orange might increase blood levels of indinavir.
One small clinical study shows that bitter orange juice slightly increases indinavir levels, but this effect is likely to be clinically insignificant. Bitter orange selectively inhibits intestinal cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4); however, the metabolism of indinavir seems to be more dependent on hepatic CYP3A4 (11269). The effect of bitter orange on other protease inhibitors has not been studied.
|
Bitter orange might increase blood levels of midazolam.
One small clinical study shows that bitter orange juice can increase midazolam levels, likely through inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) (7029). Theoretically, bitter orange might increase the risk of midazolam-related adverse effects.
|
Theoretically, taking MAOIs with synephrine-containing bitter orange preparations might increase the hypertensive effects of synephrine, potentially leading to hypertensive crisis.
|
Theoretically, bitter orange might have an additive effect when combined with drugs that prolong the QT interval, potentially increasing the risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
One case report suggests that taking bitter orange in combination with other stimulants such as caffeine might prolong the QT interval in some patients (13039).
|
Bitter orange juice might increase blood levels of sildenafil.
A small clinical study in healthy adult males shows that drinking freshly squeezed bitter orange juice 250 mL daily for 3 days and taking a single dose of sildenafil 50 mg on the 3rd day increases the peak plasma concentration of sildenafil by 18% and the overall exposure to sildenafil by 44%. Theoretically, this may be due to inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4 by bitter orange (93470).
|
Theoretically, bitter orange might increase the risk of hypertension and adverse cardiovascular effects when taken with stimulant drugs.
|
Theoretically, Ceylon cinnamon may have additive effects with antidiabetes drugs.
|
Theoretically, Ceylon cinnamon might have additive effects with antihypertensive drugs and increase the risk of hypotension.
|
Theoretically, cranberry might increase levels and adverse effects of atorvastatin.
In one case report, a patient taking atorvastatin experienced upper back pain, rhabdomyolysis, and abnormal liver function after drinking cranberry juice 16 ounces daily for 2 weeks. Theoretically, this may have been caused by inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) enzymes by cranberry juice, as atorvastatin is a CYP3A4 substrate. Creatinine kinase and liver enzymes normalized within 2 weeks of stopping cranberry juice (90042). Patients taking atorvastatin should avoid large quantities of cranberry juice.
|
Theoretically, cranberry might increase the levels and adverse effects of CYP2C9 substrates. However, research is conflicting.
There is contradictory evidence about the effect of cranberry on CYP2C9 enzymes. In vitro evidence suggests that flavonoids in cranberry inhibit CYP2C9 enzymes (10452,11115,90048). However, clinical research shows that cranberry juice does not significantly affect the levels, metabolism, or elimination of the CYP2C9 substrates flurbiprofen or diclofenac (11094,90048). Also, in patients stabilized on warfarin, drinking cranberry juice 250 mL daily for 7 days does not significantly increase the anticoagulant activity of warfarin, a CYP2C9 substrate (15374). Additional pharmacokinetic research shows that cranberry juice does not increase peak plasma concentrations or area under the concentration-time curve of warfarin (15393).
|
Theoretically, cranberry might increase the levels and adverse effects of CYP3A4 substrates.
A case of upper back pain, rhabdomyolysis, and abnormal liver function has been reported for a patient taking atorvastatin, a CYP3A4 substrate, in combination with cranberry juice 16 ounces daily for 2 weeks. Creatinine kinase and liver enzymes normalized within 2 weeks of stopping cranberry juice (90042). Also, animal research suggests that cranberry juice, administered intraduodenally 30 minutes prior to nifedipine, a CYP3A4 substrate, inhibits nifedipine metabolism and increases the area under the concentration-time curve by 1.6-fold compared to control (46420).
|
Theoretically, cranberry might modestly increase the levels and adverse effects of diclofenac.
|
Theoretically, cranberry might increase the levels and adverse effects of nifedipine.
Animal research suggests that cranberry juice, administered intraduodenally 30 minutes prior to nifedipine treatment, inhibits nifedipine metabolism and increases the area under the concentration-time curve by 1.6-fold compared to control (46420). This interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, cranberry might increase the levels and adverse effects of warfarin. However, research is conflicting.
There is contradictory evidence about the effect of cranberry juice on warfarin. Case reports have linked cranberry juice consumption to increases in the international normalized ratio (INR) in patients taking warfarin, resulting in severe spontaneous bleeding and excessive postoperative bleeding (10452,12189,12668,21187,21188,21189,46378,46396,46411)(46415,90043). Daily consumption of cranberry sauce for one week has also been linked to an increase in INR in one case report (16816). In a small study in healthy young males, taking a high dose of 3 grams of cranberry juice concentrate capsules, equivalent to 57 grams of fruit daily, for 2 weeks produced a 30% increase in the area under the INR-time curve after a single 25-mg dose of warfarin (16416). However, 3 very small clinical studies in patients stabilized on warfarin reported that cranberry juice 250 mL once or twice daily for 7 days (27% cranberry juice or pure cranberry juice) or 240 mL once daily for 14 days does not significantly increase INR or affect plasma warfarin levels (15374,17124,90045). The reasons for these discrepant findings are unclear. It is possible that the form and dose of cranberry may play a role, as cranberry extracts and juices contain different constituents. Additionally, an in vitro study evaluating 5 different cranberry juices found varying effects, with only a cranberry concentrate, and not diluted cranberry juices, inhibiting CYP2C9. However, this concentrate did not inhibit CYP2C9 activity in humans (108062).
|
Theoretically, elderberry might interfere with immunosuppressant therapy due to its immunostimulant activity.
Elderberry has immunostimulant activity, increasing the production of cytokines, including interleukin and tumor necrosis factor (10796).
|
Theoretically, elderberry might interact with pazopanib, potentially increasing the risk of adverse effects.
|
Theoretically, grape extracts may have antiplatelet effects and may increase the risk of bleeding if used with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
|
Ingesting grape juice with cyclosporine can reduce cyclosporine absorption.
A small pharmacokinetic study in healthy young adults shows that intake of purple grape juice 200 mL along with cyclosporine can decrease the absorption of cyclosporine by up to 30% when compared with water (53177). Separate doses of grape juice and cyclosporine by at least 2 hours to avoid this interaction.
|
Theoretically, grape juice might reduce the levels of CYP1A2 substrates.
A small pharmacokinetic study in healthy adults shows that ingestion of 200 mL of grape juice decreases phenacetin plasma levels. This is thought to be due to induction of CYP1A2 (2539).
|
It is unclear if grape juice or grape seed extract inhibits CYP2C9; research is conflicting.
In vitro evidence shows that grape seed extract or grape juice might inhibit CYP2C9 enzymes (11094,53011,53089). However, a small pharmacokinetic study in healthy adults shows that drinking 8 ounces of grape juice once does not affect the clearance of flurbiprofen, a probe-drug for CYP2C9 metabolism (11094). The effects of continued grape juice consumption are unclear.
|
Theoretically, grape seed extract may increase the levels of CYP2D6 substrates.
In vitro evidence suggests that grape seed extract might inhibit CYP2D6 enzymes (53011). However, this interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, grape seed extract might increase the levels of CYP2E1 substrates.
In vitro and animal research suggests that grape seed proanthocyanidin extract inhibits CYP2E1 enzymes (52949). However, this interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
It is unclear if grape seed extract inhibits or induces CYP3A4; research is conflicting.
|
Theoretically, long-term intake of grape seed extract might decrease the effects of midazolam.
Animal research shows that subchronic ingestions of grape seed extract can increase the elimination of intravenous midazolam by increasing hepatic CYP3A4 activity. Single doses of grape seed extract do not appear to affect midazolam elimination (53011).
|
Grape juice might decrease phenacetin absorption.
A small pharmacokinetic study in healthy adults shows that ingestion of 200 mL of grape juice decreases phenacetin plasma levels. This is thought to be due to induction of cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) (2539).
|
Theoretically, high doses of green tea might increase the effects and side effects of 5-fluorouracil.
Animal research shows that taking green tea in amounts equivalent to about 6 cups daily in humans for 4 weeks prior to receiving a single injection of 5-fluorouracil increases the maximum plasma levels of 5-fluorouracil by about 2.5-fold and the area under the curve by 425% (98424).
|
Theoretically, green tea might decrease the vasodilatory effects of adenosine and interfere with its use prior to stress testing.
Green tea contains caffeine. Caffeine is a competitive inhibitor of adenosine at the cellular level. However, caffeine doesn't seem to affect supplemental adenosine because high interstitial levels of adenosine overcome the antagonistic effects of caffeine (11771). It is recommended that methylxanthines and methylxanthine-containing products be stopped 24 hours prior to pharmacological stress tests (11770). However, methylxanthines appear more likely to interfere with dipyridamole (Persantine) than adenosine-induced stress testing (11771).
|
Theoretically, alcohol might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Concomitant use of alcohol and caffeine can increase caffeine serum concentrations and the risk of caffeine adverse effects. Alcohol reduces caffeine metabolism (6370).
|
Theoretically, green tea may increase the risk of bleeding if used with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
Conflicting reports exist regarding the effect of green tea on bleeding risk when used with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs; however, most evidence suggests that drinking green tea in moderate amounts is unlikely to cause a significant interaction. Green tea contains small amounts of vitamin K, approximately 7 mcg per cup (100524). Some case reports have associated the antagonism of warfarin with the vitamin K content of green tea (1460,1461,1463,4211,6048,8028,20868). However, these reports are rare, and very large doses of green tea (about 8-16 cups daily) appear to be needed to cause these effects. Furthermore, the catechins and caffeine in green tea are reported to have antiplatelet activity (733,8028,8029,12882,100524).
|
Theoretically, taking green tea with antidiabetes drugs might interfere with blood glucose control.
|
Green tea extract seems to reduce the levels and clinical effects of atorvastatin.
In healthy humans, taking green tea extract 300 mg or 600 mg along with atorvastatin reduces plasma levels of atorvastatin by approximately 24%. The elimination of atorvastatin is not affected (102714). Atorvastatin is a substrate of organic anion-transporting polypeptides (OATPs). Research shows that two of the major catechins found in green tea, epicatechin gallate (ECG) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), inhibit OATPs. Some OATPs are expressed in the small intestine and are responsible for the uptake of drugs and other compounds, which may have resulted in reduced plasma levels of atorvastatin (19079). It is not clear if drinking green tea alters the absorption of atorvastatin.
|
Green tea contains caffeine. Theoretically, concomitant use of large amounts of caffeine might increase cardiac inotropic effects of beta-agonists (15).
|
Theoretically, green tea might interfere with the effects of bortezomib.
In vitro research shows that green tea polyphenols, such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), interact with bortezomib and block its proteasome inhibitory action. This prevents the induction of cell death in multiple myeloma or glioblastoma cancer cell lines (17212). Advise patients taking bortezomib, not to take green tea.
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the effects of carbamazepine and increase the risk for convulsions.
Green tea contains caffeine. Animal research suggests that taking caffeine can lower the anticonvulsant effects of carbamazepine and can induce seizures when taken in doses above 400 mg/kg (23559,23561). Human research has shown that taking caffeine 300 mg in three divided doses along with carbamazepine 200 mg reduces the bioavailability of carbamazepine by 32% and prolongs the plasma half-life of carbamazepine 2-fold in healthy individuals (23562).
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the levels and clinical effects of celiprolol.
In a small human study, taking green tea daily for 4 days appears to decrease blood and urine levels of celiprolol by at least 98% (104607). This interaction is possibly due to the inhibition of organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP). Green tea catechins have been shown to inhibit organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATP), one of which, OATP1A2, is found in the intestine (19079,19080,98461) The interaction is thought to be due primarily to the epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) content of green tea (98461).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the effects and adverse effects of caffeine in green tea.
Green tea contains caffeine. Cimetidine can reduce caffeine clearance by 31% to 42% (11736).
|
Theoretically, green tea might increase the levels and adverse effects of clozapine and acutely exacerbate psychotic symptoms.
Animal research suggests that, although green tea extract does not affect the elimination of clozapine, it delays the time to reach peak concentration and reduces the peak plasma levels (90173). Also, concomitant administration of green tea and clozapine might theoretically cause acute exacerbation of psychotic symptoms due to the caffeine in green tea. Caffeine can increase the effects and toxicity of clozapine. Caffeine doses of 400-1000 mg daily inhibit clozapine metabolism (5051). Clozapine is metabolized by cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2). Researchers speculate that caffeine might inhibit CYP1A2. However, there is no reliable evidence that caffeine affects CYP1A2. There is also speculation that genetic factors might make some patients be more sensitive to the interaction between clozapine and caffeine (13741).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the effects and adverse effects of caffeine found in green tea.
Green tea contains caffeine. Oral contraceptives can decrease caffeine clearance by 40% to 65% (8644).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Caffeine is metabolized by cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) (3941,5051,11741,23557,23573,23580,24958,24959,24960,24962), (24964,24965,24967,24968,24969,24971,38081,48603). Theoretically, drugs that inhibit CYP1A2 may decrease the clearance rate of caffeine from green tea and increase caffeine levels.
|
Green tea is unlikely to produce clinically significant changes in the levels and clinical effects of CYP3A4 substrates.
|
Theoretically, green tea might decrease the vasodilatory effects of dipyridamole and interfere with its use prior to stress testing.
Green tea contains caffeine. Caffeine might inhibit dipyridamole-induced vasodilation (11770,11772). It is recommended that methylxanthines and methylxanthine-containing products be stopped 24 hours prior to pharmacological stress tests (11770). Methylxanthines appear more likely to interfere with dipyridamole (Persantine) than adenosine-induced stress testing (11771).
|
Theoretically, disulfiram might increase the risk of adverse effects from caffeine.
In human research, disulfiram decreases the clearance and increases the half-life of caffeine (11840).
|
Theoretically, using green tea with diuretic drugs might increase the risk of hypokalemia.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the risk for stimulant adverse effects.
|
Theoretically, estrogens might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Estrogen inhibits caffeine metabolism (2714).
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the effects of ethosuximide and increase the risk for convulsions.
Green tea contains caffeine. Animal research suggests that caffeine 92.4 mg/kg can decrease the anticonvulsant activity of ethosuximide (23560). However, this effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the effects of felbamate and increase the risk for convulsions.
Green tea contains caffeine. Animal research suggests that a high dose of caffeine 161.7 mg/kg can decreases the anticonvulsant activity of felbamate (23563). However, this effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Green tea can decrease blood levels of fexofenadine.
Clinical research shows that green tea can significantly decrease blood levels and excretion of fexofenadine. Taking green tea extract with a dose of fexofenadine decreased bioavailability of fexofenadine by about 30%. In vitro, green tea inhibits the cellular accumulation of fexofenadine by inhibiting the organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) drug transporter (111029). Research shows that two of the major catechins found in green tea, epicatechin gallate (ECG) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), inhibit OATPs, specifically OATP1A2, OATP1B1, and OATP2B1. In addition, green tea has been shown to reduce the absorption of some drugs that are OATP substrates (19079,102714,102730).
|
Theoretically, fluconazole might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Fluconazole decreases caffeine clearance by approximately 25% (11022).
|
Theoretically, green tea might increase the levels and adverse effects of flutamide.
Green tea contains caffeine. In vitro evidence suggests that caffeine can inhibit the metabolism of flutamide (23553). Theoretically, concomitant use of caffeine and flutamide might increase serum concentrations of flutamide and increase the risk adverse effects.
|
Theoretically, fluvoxamine might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Fluvoxamine reduces caffeine metabolism (6370).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might have additive adverse hepatotoxic effects.
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the levels and clinical effects of imatinib.
In animal research, a single dose of green tea extract reduces the area under the curve (AUC) of imatinib by up to approximately 64% and its main metabolite N-desmethyl imatinib by up to approximately 81% (104600). This interaction has not been shown in humans. The mechanism of action is unclear but may involve multiple pathways.
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the levels and clinical effects of lisinopril.
Preliminary clinical research shows that a single dose of green tea extract reduces plasma concentrations of lisinopril. Compared to a control group, peak levels and area under the curve (AUC) of lisinopril were reduced by approximately 71% and 66%, respectively (104599). This may be due to inhibition of organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATP) by green tea catechins (19079,19080,98461) The interaction is thought to be due primarily to the epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) content of green tea (98461).
|
Theoretically, abrupt green tea withdrawal might increase the levels and adverse effects of lithium.
|
Theoretically, metformin might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Animal research suggests that metformin can reduce caffeine metabolism (23571). Theoretically, concomitant use can increase caffeine serum concentrations and the risk of caffeine adverse effects.
|
Theoretically, methoxsalen might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Methoxsalen can reduce caffeine metabolism (23572). Concomitant use can increase caffeine serum concentrations and the risk of caffeine adverse effects.
|
Theoretically, mexiletine might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Mexiletine can decrease caffeine elimination by 50% (1260).
|
Theoretically, green tea might increase the levels and adverse effects of midazolam.
Animal research suggests that green tea extract can increase the maximum plasma concentration, but not the half-life, of oral midazolam. This effect has been attributed to the inhibition of intestinal cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) and induction of hepatic CYP3A4 enzymes by green tea constituents (20896). However, it is unlikely that this effect is clinically significant, as the dose used in animals was 50 times greater than what is commonly ingested by humans.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the risk of a hypertensive crisis.
Green tea contains caffeine. Caffeine has been shown to inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO) A and B in laboratory studies (37724,37877,37912,38108). Concomitant intake of large amounts of caffeine with MAOIs might precipitate a hypertensive crisis (15). In a case report, a patient that consumed 10-12 cups of caffeinated coffee and took the MAOI tranylcypromine presented with severe hypertension (91086). Hypertension was resolved after the patient switched to drinking decaffeinated coffee.
|
Green tea seems to reduce the levels and clinical effects of nadolol.
Preliminary clinical research shows that green tea consumption reduces plasma concentrations of nadolol. Compared to a control group, both peak levels and total drug exposure (AUC) of nadolol were reduced by approximately 85% in subjects who drank green tea daily for two weeks. Drinking green tea with nadolol also significantly reduced nadolol's systolic blood pressure lowering effect (19071). Other clinical research shows that a single dose of green tea can affect plasma nadolol levels for at least one hour (102721). Green tea catechins have been shown to inhibit organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATP), one of which, OATP1A2, is involved in the uptake of nadolol in the intestine (19071,19079,19080,98461) The interaction is thought to be due primarily to the epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) content of green tea (98461).
|
Theoretically, green tea might increase the levels and adverse effects of nicardipine.
Green tea contains EGCG. Animal research shows that EGCG increases the area under the curve (AUC) and absolute oral bioavailability of nicardipine. The mechanism of action is thought to involve inhibition of both intestinal P-glycoprotein and hepatic cytochrome P450 3A (90136). The effect of green tea itself on nicardipine is unclear.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the risk of hypertension.
Green tea contains caffeine. Concomitant use of caffeine and nicotine has been shown to have additive cardiovascular effects, including increased heart rate and blood pressure. Blood pressure was increased by 10.8/12.4 mmHg when the agents were used concomitantly (36549).
|
Green tea seems to reduce the levels of nintedanib.
Clinical research shows that green tea can significantly decrease blood levels of nintedanib. Taking green tea extract twice daily for 7 days 30 minutes prior to a meal along with nintedanib with the meal decreased the 12-hour area under the curve (AUC) values for nintedanib by 21%. There was no effect on the maximum concentration of nintedanib (111028).
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the absorption of organic anion-transporting polypeptide (OATP) substrates.
OATPs are expressed in the small intestine and liver and are responsible for the uptake of drugs and other compounds. Research shows that two of the major catechins found in green tea, epicatechin gallate (ECG) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), inhibit OATPs, specifically OATP1A2, OATP1B1, and OATP2B1. In addition, green tea has been shown to reduce the absorption of some drugs that are OATP substrates, including lisinopril, and celiprolol (19079,102714,102730).
|
Green tea might increase the levels and adverse effects of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrates.
In vitro research and case reports suggest that green tea inhibits drug efflux by P-gp, potentially increasing serum levels of P-gp substrates. Case reports from the World Health Organization (WHO) adverse drug reaction database describe increased toxicity in patients taking green tea and certain P-gp substrates (111644).
|
Theoretically, green tea might decrease the effects of pentobarbital.
Green tea contains caffeine. Theoretically, caffeine might negate the hypnotic effects of pentobarbital (13742).
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the effects of phenobarbital and increase the risk for convulsions.
|
Theoretically, phenothiazines might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
|
Theoretically, phenylpropanolamine might increase the risk of hypertension, as well as the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the effects of phenytoin and increase the risk for convulsions.
|
Theoretically, green tea might increase the levels and clinical effects of pioglitazone.
Green tea contains caffeine. Animal research suggests that caffeine can modestly increase the maximum concentration, area under the curve, and half-life of pioglitazone, and also reduce its clearance. This increased the antidiabetic effects of pioglitazone (108812). However, the exact mechanism of this interaction is unclear.
|
Theoretically, quinolone antibiotics might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the levels and adverse effects of both caffeine and riluzole.
Green tea contains caffeine. Caffeine and riluzole are both metabolized by cytochrome P450 1A2, and concomitant use might reduce metabolism of one or both agents (11739).
|
Theoretically, green tea extract might alter the absorption and distribution of rosuvastatin.
In animal research, giving green tea extract with rosuvastatin increased plasma levels of rosuvastatin. Rosuvastatin is a substrate of organic anion-transporting polypeptide (OATP)1B1, which is expressed in the liver. The increased plasma levels may have been related to inhibition of OATP1B1 (102717). However, in humans, taking EGCG with rosuvastatin reduced plasma levels of rosuvastatin, suggesting an inhibition of intestinal OATP (102730). It is not clear if drinking green tea alters the absorption of rosuvastatin.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase stimulant adverse effects.
Green tea contains caffeine. Due to the central nervous system (CNS) stimulant effects of caffeine, concomitant use with stimulant drugs can increase the risk of adverse effects (11832).
|
Theoretically, terbinafine might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Terbinafine decreases the clearance of intravenous caffeine by 19% (11740).
|
Theoretically, green tea might increase the levels and adverse effects of theophylline.
Green tea contains caffeine. Large amounts of caffeine might inhibit theophylline metabolism (11741).
|
Theoretically, green tea might increase the levels and adverse effects of tiagabine.
Green tea contains caffeine. Animal research suggests that chronic caffeine administration can increase the serum concentrations of tiagabine. However, concomitant use does not seem to reduce the antiepileptic effects of tiagabine (23561).
|
Theoretically, ticlopidine might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Green tea contains caffeine. In vitro evidence suggests that ticlopidine can inhibit caffeine metabolism (23557). However, this effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, green tea might reduce the effects of valproate and increase the risk for convulsions.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the levels and adverse effects of both verapamil and caffeine.
Animal research suggests that the green tea constituent EGCG increases the area under the curve (AUC) values for verapamil by up to 111% and its metabolite norverapamil by up to 87%, likely by inhibiting P-glycoprotein (90138). Also, theoretically, concomitant use of verapamil and caffeinated beverages such as green tea might increase plasma caffeine concentrations and the risk of adverse effects, due to the caffeine contained in green tea. Verapamil increases plasma caffeine concentrations by 25% (11741).
|
Theoretically, green tea may increase the risk of bleeding if used with warfarin.
Conflicting reports exist regarding the potential of green tea to antagonize the effect of warfarin; however, most evidence suggests that drinking green tea in moderation is unlikely to cause a significant interaction. Green tea contains a small amount of vitamin K, approximately 7 mcg per cup (100524). Some case reports have associated the antagonism of warfarin with the vitamin K content of green tea (1460,1461,1463,4211,6048,8028,20868). However, these reports are rare, and very large doses of green tea (about 8-16 cups daily) appear to be needed to cause these effects (1460,1461,1463,8028). Therefore, use of green tea in moderate amounts is unlikely to antagonize the effects of warfarin; however, very large doses should be avoided.
|
Theoretically, guarana might decrease the vasodilatory effects of adenosine and interfere with its use prior to stress testing.
Guarana contains caffeine. Caffeine is a competitive inhibitor of adenosine at the cellular level. However, caffeine does not seem to affect supplemental adenosine because high interstitial levels of adenosine overcome the antagonistic effects of caffeine (11771). It is recommended that methylxanthines and methylxanthine-containing products be stopped 24 hours prior to pharmacological stress tests (11770). However, methylxanthines appear more likely to interfere with dipyridamole (Persantine) than adenosine-induced stress testing (11771).
|
Theoretically, alcohol might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Guarana contains caffeine. Concomitant use of alcohol can increase caffeine serum concentrations and the risk of caffeine adverse effects. Alcohol reduces caffeine metabolism (6370).
|
Theoretically, guarana may increase the risk of bleeding if used with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
|
Theoretically, taking guarana with antidiabetes drugs might interfere with blood glucose control.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the clinical effects of beta-adrenergic agonists.
Guarana contains caffeine. Theoretically, concomitant use of large amounts of caffeine might increase cardiac inotropic effects of beta-agonists (15).
|
Theoretically, guarana might reduce the effects of carbamazepine and increase the risk for convulsions.
Animal research suggests that taking caffeine can lower the anticonvulsant effects of carbamazepine and can induce seizures when given to animals in doses above 400 mg/kg (23559,23561). Human research has shown that taking caffeine 300 mg in three divided doses along with carbamazepine 200 mg reduces the bioavailability of carbamazepine by 32% and prolongs the plasma half-life of carbamazepine two-fold in healthy individuals (23562).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the effects and adverse effects of caffeine in guarana.
Guarana contains caffeine. Cimetidine decreases the rate of caffeine clearance by 31% to 42% (11736).
|
Theoretically, guarana might increase the levels and adverse effects of clozapine and acutely exacerbate psychotic symptoms.
Guarana contains caffeine. Caffeine can increase the effects and toxicity of clozapine. Caffeine doses of 400-1000 mg per day inhibit clozapine metabolism (5051). Clozapine is metabolized by cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2). Researchers speculate that caffeine might inhibit CYP1A2. However, there is no reliable evidence that caffeine affects CYP1A2. There is also speculation that genetic factors might make some patients more sensitive to the interaction between clozapine and caffeine (13741).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the effects and adverse effects of caffeine found in guarana.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
|
Theoretically, guarana might decrease the vasodilatory effects of dipyridamole and interfere with its use prior to stress testing.
Guarana contains caffeine. Caffeine might inhibit dipyridamole-induced vasodilation (11770,11772). It is recommended that methylxanthines and methylxanthine-containing products be stopped 24 hours prior to pharmacological stress tests (11770). Methylxanthines appear more likely to interfere with dipyridamole than adenosine-induced stress testing (11771).
|
Theoretically, disulfiram might increase the risk of adverse effects from caffeine.
In human research, disulfiram decreases the clearance and increases the half-life of caffeine (11840).
|
Theoretically, using guarana with diuretic drugs might increase the risk of hypokalemia.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the risk for stimulant adverse effects.
Guarana contains caffeine. Use of ephedrine with caffeine can increase the risk of stimulatory adverse effects. There is evidence that using ephedrine with caffeine might increase the risk of serious life-threatening or debilitating adverse effects such as hypertension, myocardial infarction, stroke, seizures, and death (1275,6486,10307).
|
Theoretically, estrogens might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Guarana contains caffeine. Estrogen inhibits caffeine metabolism (2714).
|
Theoretically, guarana might reduce the effects of ethosuximide and increase the risk for convulsions.
Guarana contains caffeine. Animal research shows that caffeine 92.4 mg/kg can decrease the anticonvulsant activity of ethosuximide (23560). This effect has not been observed in humans.
|
Theoretically, guarana might reduce the effects of felbamate and increase the risk for convulsions.
Guarana contains caffeine. Animal research shows that a high dose of caffeine 161.7 mg/kg can decreases the anticonvulsant activity of felbamate (23563). This effect has not been observed in humans.
|
Theoretically, fluconazole might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Guarana contains caffeine. Fluconazole decreases caffeine clearance by approximately 25% (11022).
|
Theoretically, guarana might increase the levels and adverse effects of flutamide.
Guarana contains caffeine. In vitro evidence shows that caffeine can inhibit the metabolism of flutamide (23553). However, this effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, fluvoxamine might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Guarana contains caffeine. Fluvoxamine reduces caffeine metabolism (6370).
|
Theoretically, abrupt guarana withdrawal might increase the levels and adverse effects of lithium.
|
Theoretically, metformin might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Guarana contains caffeine. Animal research shows that metformin can reduce caffeine metabolism (23571). However, this effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, methoxsalen might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Guarana contains caffeine. Methoxsalen can reduce caffeine metabolism (23572).
|
Theoretically, mexiletine might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the risk of a hypertensive crisis.
Guarana contains caffeine. Caffeine has been shown to inhibit MAO-A and -B in laboratory studies (37724,37877,37912,38108). Concomitant intake of large amounts of caffeine with MAOIs might precipitate a hypertensive crisis (15). In a case report, a patient that consumed 10-12 cups of caffeinated coffee and took the MAOI tranylcypromine presented with severe hypertension (91086). Hypertension was resolved after the patient switched to drinking decaffeinated coffee.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the risk of hypertension.
Guarana contains caffeine. Concomitant use of caffeine and nicotine has been shown to have additive cardiovascular effects, including increased heart rate and blood pressure. Blood pressure was increased by 10.8/12.4 mmHg when the agents were used concomitantly (36549).
|
Theoretically, guarana might decrease the effects of pentobarbital.
|
Theoretically, guarana might reduce the effects of phenobarbital and increase the risk for convulsions.
|
Theoretically, phenothiazines might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
|
Theoretically, phenylpropanolamine might increase the risk of hypertension, as well as the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
|
Theoretically, guarana might reduce the effects of phenytoin and increase the risk for convulsions.
|
Theoretically, guarana might increase the levels and clinical effects of pioglitazone.
Guarana contains caffeine. Animal research suggests that caffeine can modestly increase the maximum concentration, area under the curve, and half-life of pioglitazone, and also reduce its clearance. This increased the antidiabetic effects of pioglitazone (108812). However, the exact mechanism of this interaction is unclear.
|
Theoretically, quinolone antibiotics might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase the levels and adverse effects of both caffeine and riluzole.
Guarana contains caffeine. Caffeine and riluzole are both metabolized by cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2), and concomitant use might reduce the metabolism of one or both agents (11739).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might increase stimulant adverse effects.
Guarana contains caffeine. Due to the central nervous system (CNS) stimulant effects of caffeine, concomitant use with stimulant drugs can increase the risk of adverse effects (11832).
|
Theoretically, terbinafine might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Guarana contains caffeine. Terbinafine decreases the clearance of intravenous caffeine by 19% (11740).
|
Theoretically, guarana might increase the levels and adverse effects of theophylline.
Guarana contains caffeine. Large amounts of caffeine might decrease theophylline clearance by 23% to 29% (11741).
|
Theoretically, guarana might increase the levels and adverse effects of tiagabine.
Guarana contains caffeine. Animal research shows that chronic caffeine administration can increase the serum concentrations of tiagabine. However, concomitant use does not seem to reduce the antiepileptic effects of tiagabine (23561).
|
Theoretically, ticlopidine might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Guarana contains caffeine. In vitro evidence shows that ticlopidine can inhibit the metabolism of caffeine (23557). However, this interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, guarana might reduce the effects of valproate and increase the risk for convulsions.
|
Theoretically, verapamil might increase the levels and adverse effects of caffeine.
Verapamil increases plasma caffeine concentrations by 25% (11741).
|
Theoretically, hawthorn may increase the risk of bleeding if used with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
In vitro and animal research shows that hawthorn can inhibit platelet aggregation (95528,95529,95530,95531). However, its effect in humans is unclear. One observational study shows that patients taking hawthorn shortly before undergoing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery or valve replacement surgery have a 10% incidence of postoperative bleeding, compared with 1% in those who never consumed hawthorn extract (95527). However, clinical research shows that taking a specific preparation of dried hawthorn leaves and flowers (Crataesor, Soria Natural Lab) 800 mg three times daily for 15 days does not affect platelet aggregation or levels of thromboxane B2, the metabolite of thromboxane A2, in healthy humans (54664).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might cause additive effects on blood pressure and heart rate.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might cause additive coronary vasodilation and hypotensive effects.
|
Theoretically, hawthorn might potentiate the effects and adverse effects of digoxin.
Hawthorn appears to improve cardiac output (12595); however, hawthorn does not appear to affect digoxin pharmacokinetics (19249). Case reports suggest that at least one species of hawthorn root extract (Crataegus mexicana) may produce adverse effects similar to digoxin and can cross-react with digoxin assays, leading to falsely elevated plasma digoxin levels (113112,113113).
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might cause additive coronary vasodilatory effects.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use might result in additive vasodilation and hypotension.
Hawthorn might inhibit PDE-5 and cause vasodilation (12595).
|
Although Panax ginseng has shown antiplatelet effects in the laboratory, it is unlikely to increase the risk of bleeding if used with anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
In vitro evidence suggests that ginsenoside constituents in Panax ginseng might decrease platelet aggregation (1522,11891). However, research in humans suggests that ginseng does not affect platelet aggregation (11890). Animal research indicates low oral bioavailability of Rb1 and rapid elimination of Rg1, which might explain the discrepancy between in vitro and human research (11153). Until more is known, use with caution in patients concurrently taking anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs.
|
Theoretically, taking Panax ginseng with antidiabetes drugs might increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Clinical research suggests that Panax ginseng might decrease blood glucose levels (89740). Monitor blood glucose levels closely.
|
Theoretically, taking Panax ginseng with caffeine might increase the risk of adverse stimulant effects.
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng might decrease levels of drugs metabolized by CYP1A1.
In vitro research shows that Panax ginseng can induce the CYP1A1 enzyme (24104).
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng might increase levels of drugs metabolized by CYP2D6. However, research is conflicting.
There is some evidence that Panax ginseng can inhibit the CYP2D6 enzyme by approximately 6% (1303,51331). In addition, in animal research, Panax ginseng inhibits the metabolism of dextromethorphan, a drug metabolized by CYP2D6, by a small amount (103478). However, contradictory research suggests Panax ginseng might not inhibit CYP2D6 (10847). Until more is known, use Panax ginseng cautiously in patients taking drugs metabolized by these enzymes.
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng might increase or decrease levels of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4.
Panax ginseng may affect the clearance of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4. One such drug is imatinib. Inhibition of CYP3A4 was believed to be responsible for a case of imatinib-induced hepatotoxicity (89764). In contrast, Panax ginseng has been shown to increase the clearance of midazolam, another drug metabolized by CYP3A4 (89734,103478). Clinical research shows that Panax ginseng can reduce midazolam area under the curve by 44%, maximum plasma concentration by 26%, and time to reach maximum plasma concentration by 29% (89734). Midazolam metabolism was also increased in animals given Panax ginseng (103478). Until more is known, use Panax ginseng cautiously in combination with CYP3A4 substrates.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use of large amounts of Panax ginseng might interfere with hormone replacement therapy.
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng might decrease blood levels of oral or intravenous fexofenadine.
Animal research suggests that taking Panax ginseng in combination with oral or intravenous fexofenadine may reduce the bioavailability of fexofenadine. Some scientists have attributed this effect to the ability of Panax ginseng to increase the expression of P-glycoprotein (24101).
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng might reduce the effects of furosemide.
There is some concern that Panax ginseng might contribute to furosemide resistance. There is one case of resistance to furosemide diuresis in a patient taking a germanium-containing ginseng product (770).
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng might increase the effects and adverse effects of imatinib.
A case of imatinib-induced hepatotoxicity has been reported for a 26-year-old male with chronic myelogenous leukemia stabilized on imatinib for 7 years. The patient took imatinib 400 mg along with a Panax ginseng-containing energy drink daily for 3 months. Since imatinib-associated hepatotoxicity typically occurs within 2 years of initiating therapy, it is believed that Panax ginseng affected imatinib toxicity though inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4. CYP3A4 is the primary enzyme involved in imatinib metabolism (89764).
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng use might interfere with immunosuppressive therapy.
Panax ginseng might have immune system stimulating properties (3122).
|
Theoretically, taking Panax ginseng with insulin might increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Clinical research suggests that Panax ginseng might decrease blood glucose levels (89740). Insulin dose adjustments might be necessary in patients taking Panax ginseng; use with caution.
|
Although Panax ginseng has demonstrated variable effects on cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), which metabolizes lopinavir, Panax ginseng is unlikely to alter levels of lopinavir/ritonavir.
Lopinavir is metabolized by CYP3A4 and is administered with the CYP3A4 inhibitor ritonavir to increase its plasma concentrations. Panax ginseng has shown variable effects on CYP3A4 activity in humans (89734,89764). However, taking Panax ginseng (Vitamer Laboratories) 500 mg twice daily for 14 days did not alter the pharmacokinetics of lopinavir/ritonavir in 12 healthy volunteers (93578).
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng may increase the clearance of midazolam.
Midazolam is metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4). Clinical research suggests that Panax ginseng can reduce midazolam area under the curve by 44%, maximum plasma concentration by 26%, and time to reach maximum plasma concentration by 29% (89734). Midazolam metabolism was also increased in animals given Panax ginseng (103478).
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng can interfere with MAOI therapy.
|
Theoretically, taking Panax ginseng with nifedipine might increase serum levels of nifedipine and the risk of hypotension.
Preliminary clinical research shows that concomitant use can increase serum levels of nifedipine in healthy volunteers (22423). This might cause the blood pressure lowering effects of nifedipine to be increased when taken concomitantly with Panax ginseng.
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng has an additive effect with drugs that prolong the QT interval and potentially increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmias. However, research is conflicting.
|
Theoretically, taking Panax ginseng with raltegravir might increase the risk of liver toxicity.
A case report suggests that concomitant use of Panax ginseng with raltegravir can increase serum levels of raltegravir, resulting in elevated liver enzymes levels (23621).
|
Theoretically, Panax ginseng might increase or decrease levels of selegiline, possibly altering the effects and side effects of selegiline.
Animal research shows that taking selegiline with a low dose of Panax ginseng extract (1 gram/kg) reduces selegiline bioavailability, while taking a high dose of Panax ginseng extract (3 grams/kg) increases selegiline bioavailability (103053). More research is needed to confirm these effects.
|
Theoretically, taking Panax ginseng with stimulant drugs might increase the risk of adverse stimulant effects.
|
Panax ginseng might affect the clearance of warfarin. However, this interaction appears to be unlikely.
There has been a single case report of decreased effectiveness of warfarin in a patient who also took Panax ginseng (619). However, it is questionable whether Panax ginseng was the cause of this decrease in warfarin effectiveness. Some research in humans and animals suggests that Panax ginseng does not affect the pharmacokinetics of warfarin (2531,11890,17204,24105). However, other research in humans suggests that Panax ginseng might modestly increase the clearance of the S-warfarin isomer (15176). More evidence is needed to determine whether Panax ginseng causes a significant interaction with warfarin.
|
Theoretically, royal jelly might increase the risk of hypotension when taken with antihypertensive drugs.
|
Royal jelly might increase the risk of bleeding when taken with warfarin.
In one case, an 87-year-old male who was previously stabilized on warfarin developed hematuria and was found to have an INR of 7.29 after taking a royal jelly supplement for one week (14303).
|
Theoretically, a high intake of dietary sodium might reduce the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs.
|
Concomitant use of mineralocorticoids and some glucocorticoids with sodium supplements might increase the risk of hypernatremia.
Mineralocorticoids and some glucocorticoids (corticosteroids) cause sodium retention. This effect is dose-related and depends on mineralocorticoid potency. It is most common with hydrocortisone, cortisone, and fludrocortisone, followed by prednisone and prednisolone (4425).
|
Altering dietary intake of sodium might alter the levels and clinical effects of lithium.
High sodium intake can reduce plasma concentrations of lithium by increasing lithium excretion (26225). Reducing sodium intake can significantly increase plasma concentrations of lithium and cause lithium toxicity in patients being treated with lithium carbonate (26224,26225). Stabilizing sodium intake is shown to reduce the percentage of patients with lithium level fluctuations above 0.8 mEq/L (112909). Patients taking lithium should avoid significant alterations in their dietary intake of sodium.
|
Concomitant use of sodium-containing drugs with additional sodium from dietary or supplemental sources may increase the risk of hypernatremia and long-term sodium-related complications.
The Chronic Disease Risk Reduction (CDRR) intake level of 2.3 grams of sodium daily indicates the intake at which it is believed that chronic disease risk increases for the apparently healthy population (100310). Some medications contain high quantities of sodium. When used in conjunction with sodium supplements or high-sodium diets, the CDRR may be exceeded. Additionally, concomitant use may increase the risk for hypernatremia; this risk is highest in the elderly and people with other risk factors for electrolyte disturbances.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use of tolvaptan with sodium might increase the risk of hypernatremia.
Tolvaptan is a vasopressin receptor 2 antagonist that is used to increase sodium levels in patients with hyponatremia (29406). Patients taking tolvaptan should use caution with the use of sodium salts such as sodium chloride.
|
Theoretically, stevia might increase the risk for hypoglycemia when combined with antidiabetes drugs.
Preliminary clinical research in patients with type 2 diabetes suggests that taking a single dose of stevia extract 1000 mg reduces postprandial blood glucose levels when taken with a meal (11812). However, other clinical research in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes suggests that taking stevioside 250 mg three times daily does not significantly affect blood glucose levels or glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) after three months of treatment (16705).
|
Theoretically, combining stevia or stevia constituents with antihypertensive agents might increase the risk of hypotension.
|
Theoretically, stevia might decrease clearance and increase levels of lithium.
|
Theoretically, combining yohimbe bark with antiplatelet or anticoagulant drugs might have additive effects; however, this has not been reported in clinical research.
Research in healthy adults shows that taking yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe bark, in doses of 8 mg or more, seems to inhibit platelet aggregation in vitro by binding to the alpha-2 adrenoceptor (86773,86806,86835,86853). The effects of yohimbe bark itself are unclear; yohimbe bark contains 0.6% to 1.38% yohimbine, but it is unclear how much is absorbed (86862,89263).
|
Theoretically, yohimbe might reduce the effects of antihypertensive drugs.
|
Theoretically, yohimbe might precipitate clonidine withdrawal.
Chronic clonidine use can downregulate alpha-2 adrenoreceptors. Animal research and one human case report suggest that concomitant administration of yohimbine, an alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonist, may precipitate clonidine withdrawal and lead to sympathomimetic toxicity, including hypertensive crisis (111406).
|
Theoretically, yohimbe might decrease the levels and clinical effects of CYP1A2 substrates.
In vitro research shows that yohimbe extract induces CYP1A2 enzymes (111404).
|
CYP2D6 inhibitors may increase the levels and adverse effects of yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe.
In vitro and clinical research shows that the yohimbe bark constituent, yohimbine, is metabolized by CYP2D6 isoenzymes (105688,105697,105698). Paroxetine, a cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 inhibitor, increases the maximum serum concentration of yohimbine and reduces the clearance of yohimbine compared to yohimbine alone in patients who are extensive CYP2D6 metabolizers. (114932).
|
Theoretically, yohimbe might increase the levels and adverse effects of CYP2D6 substrates.
In vitro research suggests that yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe bark, inhibits CYP2D6 enzyme activity (23117).
|
Theoretically, CYP3A4 inhibitors might increase the levels and adverse effects of yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe bark.
|
Theoretically, yohimbe might decrease the levels and clinical effects of CYP3A4 substrates.
In vitro research shows that yohimbe extract induces CYP3A4 enzymes (111404).
|
Concomitant use of MAOIs with yohimbe can result in additive effects.
|
Paroxetine decreases the clearance of yohimbine and may increase its effects.
Paroxetine, a cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 inhibitor, increases the maximum serum concentration of yohimbine by about 350% and reduces the clearance of yohimbine by about 80% compared to yohimbine alone in patients who are extensive CYP2D6 metabolizers. No significant changes in pharmacokinetic parameters of yohimbine were observed with coadministration of paroxetine in patients who are poor CYP2D6 metabolizers (114932).
|
Theoretically, using yohimbine with phenothiazines might have additive effects.
Yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, has alpha-2 adrenergic antagonist effects. Theoretically, combining it with phenothiazines can cause additive alpha-2 adrenergic antagonism (19).
|
Theoretically, taking yohimbe with stimulant drugs can have additive effects.
|
Theoretically, taking yohimbe with TCAs can increase adverse effects.
A small clinical study in patients taking TCAs for at least 4 weeks shows that receiving doses of intravenous yohimbine 2.5-20 mg daily for up to 7 days precipitates severe anxiety, agitation, and tremor (105881). The effects of yohimbe bark itself are unclear; oral yohimbe bark contains 0.6% to 1.38% yohimbine, but it is unclear how much is absorbed (86862,89263).
|
Below is general information about the adverse effects of the known ingredients contained in the product RAW Tea. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
General
...Orally, bee pollen seems to be well tolerated in most patients.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Acute hepatitis, allergic reactions, interstitial nephritis, kidney failure.
Dermatologic ...Orally, a case of photosensitivity has been reported for a 32-year-old patient who took a dietary supplement containing ginseng, goldenseal, bee pollen, and other ingredients. Symptoms included a pruritic, erythematous rash that was localized to the sun-exposed surfaces of the neck and extremities. Following treatment with topical and subcutaneous corticosteroids and discontinuation of the supplement, the skin rash slowly resolved. It is not known if this effect was due to the bee pollen, one of the other ingredients, or their combination (33954).
Hepatic ...Orally, there have been two cases of acute hepatitis associated with bee pollen use. One case involved ingestion of two tablespoons of pure bee pollen daily for several months. Another case involved ingestion of 14 tablets per day of a combination herbal product containing bee pollen, chaparral, and 19 other herbs for 6 weeks (1351). In this case, it is not known if bee pollen or another herb might have caused the adverse event.
Immunologic
...Patients with a history of seasonal pollen allergies, particularly allergies to plants in the Asteraceae/Compositae family, including ragweed, chrysanthemums, marigolds, daisies, and many other herbs, are at risk for serious allergic reactions to oral bee pollen.
Allergic reactions can include itching, swelling, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, and anaphylaxis (5,6,11,13480,33952,33965,91981,91984,109991). In one case, exercise may have contributed to the reaction. A 15-year-old male developed generalized urticaria, facial angioedema, and dyspnea 30 minutes into a vigorous exercise session and an hour after ingesting bee pollen granules. The patient experienced abdominal cramps within minutes of consuming bee pollen on 3 previous occasions and had a positive skin prick test for bee pollen after the anaphylactic reaction (109991). Allergy symptoms due to chronic intake of bee pollen include gastrointestinal and neurologic symptoms and eosinophilia (2627,33964).
A case of allergic eosinophilic gastropathy has been reported for a 5 year-old child who was given bee pollen daily to strengthen the immune system. Symptoms included abdominal pain, vomiting, and swelling of the eyelids and legs (91981).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, there is one report of dizziness in a patient who took a combination product containing royal jelly, bee pollen extract, and a bee pollen plus pistil extract (12008). It is not known if this effect was due to the bee pollen, another ingredient, or the combination.
Renal ...Orally, there is one report of a patient taking a bee pollen-containing supplement for greater than 5 months who developed breathing difficulties, edema with weight gain, and loss of appetite. The patient was diagnosed with interstitial nephritis and drug-induced acute kidney failure. The supplement was discontinued and the patient was started on hemodialysis. The patient improved after several sessions of hemodialysis (18068).
Other ...Although some research has shown a lack of mycotoxins in twenty samples of bee pollen, analysis of other ready-to-eat bee pollen products have revealed contamination with potential mycotoxin producing species, including Penicillium verrucosum, Aspergillus niger aggregate, Aspergillus carbonarius, Aspergillus ochraceus, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus parasiticus, and Alternaria spp. (33959,33961).
General
...Orally, beet seems to be well tolerated when used for medicinal purposes, short term.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Red stools and red urine.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Hypocalcemia and kidney damage when ingested in large amounts.
Endocrine ...Theoretically, ingestion of large quantities of beets could lead to hypocalcemia because of the oxaluric acid content (18).
Gastrointestinal
...Orally, beet juice may cause red stools (94470,97726,100142,100145,105762).
This red coloring of the stools is not harmful. Additionally, beet supplementation has been reported to cause black stools. In one case, a 79-year-old male on apixaban and clopidogrel presented with black stools, nausea, and vomiting after taking beet pills 2-3 days prior. The likelihood of upper gastrointestinal bleed was determined to be low based on factors such as normal vital signs and lack of severe anemia. The patient was diagnosed with beet-induced pseudo-hematochezia which was successfully treated with fluids and discontinuation of the beet supplement (113426).
Other less common gastrointestinal side effects include loose stools, constipation, and nausea (100149).
Genitourinary ...Orally, beet is known to produce red or pink urine (beeturia) in some people (32569,34134,94464,94470,97725,97726,100142,100145,100152,105762,113422). However, this red coloring of the urine is not harmful and dissipates after about 12 hours (113422).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, vivid dreams and worsening headaches have each occurred in one person in a clinical trial, although it is not clear if this is due to beet (97723).
Renal ...Theoretically, ingestion of large quantities of beets could lead to kidney damage due to its oxaluric acid content (18).
General
...Orally, bilberry fruit, juice, and extracts seem to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Dark-colored stools, flatulence, and gastrointestinal discomfort.
Gastrointestinal
...In one small clinical trial, mild-to-moderate flatulence was reported in 33% of patients taking sieved bilberries and concentrated bilberry juice (91506).
However, the patients in this study had ulcerative colitis, and the study lacked a control group, limiting the validity of this finding. In another small clinical study of males with age-related cognitive impairment, temporary adverse gastrointestinal (GI) effects were reported in 13% of patients drinking a combination of bilberry and grape juice. However, the adverse GI effect rate was identical in patients drinking a placebo juice (110641). A post-marketing surveillance report of 2295 patients using bilberry extract (Tegens) found that 1% of patients complained of GI discomfort and less than 1% experienced nausea or heartburn (35500).
Theoretically, fresh bilberry fruit may have laxative effects. One clinical trial noted an increased frequency of bowel movements following the administration of a combination formulation containing aerial agrimony parts, cinnamon quills, powdered bilberry fruit, and slippery elm bark (35462). It is unclear if these effects were due to bilberry, other ingredients, or the combination.
Other ...Orally, bilberry may cause discoloration of feces and the tongue. In one study, a dark-bluish to black discoloration of both the feces and the tongue was observed following consumption of sieved bilberries and concentrated bilberry juice. In one patient, a slight discoloration of the teeth has also been observed (91506). In another study, 50% of patients reported dark green stools after taking bilberry extract 700 mg twice daily for 4 weeks (104194).
General
...Orally, bitter orange might be unsafe when used in medicinal amounts.
Topically and when inhaled as aromatherapy, bitter orange seems to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Hypertension and tachycardia, particularly when used in combination with caffeine and/or other stimulant ingredients.
Topically: Skin irritation.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Myocardial infarction, QT prolongation, seizures, stroke, syncope, tachyarrhythmia, and ventricular fibrillation have been reported in patients taking bitter orange in combination with other ingredients. It is unclear if these effects are due to bitter orange, other ingredients, or the combination.
Cardiovascular
...Bitter orange, which contains adrenergic agonists synephrine and octopamine, may cause hypertension and cardiovascular toxicity when taken orally (2040,6969,6979).
Studies evaluating the effect of bitter orange on cardiovascular parameters have been mixed. Several studies show that taking bitter orange alone or in combination with caffeine increases blood pressure and heart rate. In one clinical study, bitter orange in combination with caffeine increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure and heart rate in otherwise healthy normotensive adults (13657). In another study, a single dose of bitter orange 900 mg, standardized to 6% synephrine (54 mg), also increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure and heart rate for up to 5 hours in young, healthy adults (13774). Using half that dose of bitter orange and providing half as much synephrine, did not seem to significantly increase blood pressure or QT interval in healthy adults (14311). Increased diastolic, but not systolic, blood pressure or heart rate also occurred in a clinical trial involving a specific supplement containing synephrine 21 mg and caffeine 304 mg (Ripped Fuel Extreme Cut, Twinlab) (35743). Synephrine given intravenously to males increased systolic blood pressure, but lacked an effect on diastolic blood pressure or heart rate (12193).
In clinical research and case reports, tachycardia, tachyarrhythmia, QT prolongation, ischemic stroke, variant angina, and myocardial infarction have occurred with use of bitter orange or synephrine-containing multi-ingredient products (12030,13039,13067,13091,13657,14326,35749,91680). In one case report, a combination product containing bitter orange may have masked bradycardia and hypotension while exacerbating weight loss in a 16 year-old female with an eating disorder taking the product for weight loss (35740). From 1998 to 2004, Health Canada received 16 reports of serious adverse cardiovascular reactions such as tachycardia, cardiac arrest, ventricular fibrillation, blackout, and collapse. In two of these cases, the patient died. In almost all of these cases, bitter orange was combined with another stimulant such as caffeine, ephedrine, or both (14342).
Other research has found no significant effect of bitter orange on blood pressure or heart rate. Several clinical studies have reported that, when taken as a single dose or in divided doses ranging from 20-100 mg for one day, p-synephrine had no significant effect on blood pressure, heart rate, electrocardiogram results or adverse cardiovascular events in healthy adults (35772,91681,91681,95659,101708) Similarly, no difference in blood pressure, heart rate or electrocardiogram results were reported when p-synephrine from bitter orange (Advantra Z/Kinetic; Nutratech/Novel Ingredients Inc.) was taken for 6 weeks in healthy patients (11268). Another clinical study showed no significant effect of bitter orange (Nutratech Inc.), standardized to synephrine 20 mg, on blood pressure or heart rate when taken daily for 8 weeks in healthy males (95656). In other research, changes in blood pressure, heart rate, or QTc interval were lacking when bitter orange was given alone or in combination with caffeine and green tea (14311,35753,35755,35764,35769,35770). In one study of healthy adults, taking a single dose of p-synephrine 103 mg actually reduced mean diastolic blood pressure by 0.4-4 mmHg at 1 and 2 hours after administration when compared with placebo (95659).
A meta-analysis of clinical trials in adults with or without obesity suggests that taking p-synephrine 6-214 mg orally daily does not affect blood pressure or heart rate when used short-term, but modestly increases blood pressure and heart rate when taken for 56-60 days (109950).
The effect of bitter orange on blood pressure, heart rate, and electrocardiogram results in patients with underlying conditions, particularly cardiovascular disease, is unknown and requires further study.
Dermatologic ...Photosensitivity may occur, particularly in fair-skinned people (11909). In a clinical trial, topical application with bitter orange essential oil resulted in irritation (6972).
Endocrine ...Some clinical research shows that taking a specific supplement containing 21 mg of synephrine and 304 mg of caffeine (Ripped Fuel Extreme Cut, Twinlab) increases levels of postprandial glucose (35743). Other preliminary clinical research shows that taking a specific pre-workout supplement (Cellucor C4 Pre-Workout, Nutrabolt) along with a bitter orange extract standardized for synephrine 20 mg (Nutratech Inc.) 30 minutes once before exercise causes a significant 12% increase in glucose (95657); however, there is no difference in blood glucose when compared with placebo when this combination is taken daily for 8 weeks (95656). The effect of bitter orange itself is unclear.
Gastrointestinal ...Bitter orange has been linked to a report of ischemic colitis. In one case, a 52-year-old female developed ischemic colitis after taking a bitter orange-containing supplement (NaturalMax Skinny Fast, Nutraceutical Corporation) for a week. Symptoms resolved within 48 hours after discontinuing the supplement (15186). As this product contains various ingredients, the effect of bitter orange itself is unclear.
Musculoskeletal ...Unsteady gait has been noted in one case report of a patient taking bitter orange (13091). In another case, an otherwise healthy, Black male with sickle cell trait, developed severe rhabdomyolysis following ingestion of a specific weight loss product (Lipo 6, Nutrex Research Inc.), which contained synephrine and caffeine (16054). However, other preliminary clinical research shows that taking a specific pre-workout supplement (Cellucor C4 Pre-Workout, Nutrabolt) along with a bitter orange extract standardized for synephrine 20 mg (Nutratech Inc.), taken 30 minutes once before exercise (95657) or daily for 8 weeks, does not affect creatine kinase or serum creatinine levels when compared with placebo (95656). As these products contain various ingredients, the effect of bitter orange itself is unclear.
Neurologic/CNS ...Dizziness, difficulty in concentrating, memory loss, syncope, seizure, and stroke have been noted in case reports following bitter orange administration (13091,13039). Theoretically, bitter orange may trigger a migraine or cluster headache due to its synephrine and octopamine content (35768). When used as aromatherapy, bitter orange essential oil has also been reported to cause headache in some patients (104187). Sprint athletes taking the bitter orange constituent p-synephrine 3 mg/kg (Synephrine HCL 99%, Nutrition Power) 60 minutes before exercises and sprinting reported more nervousness (mean difference 0.9) when compared with placebo on a Likert scale. Although statistically significant, this difference is not considered clinically significant (95655).
General
...Orally, Ceylon cinnamon is generally well tolerated, and adverse reactions are uncommon.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Bloating, dyspepsia, nausea.
Topically: Allergic dermatitis, irritation of mucous membranes and skin.
Dermatologic
...Orally, a case of systemic contact dermatitis has been reported in a patient who consumed cinnamon (type not specified) after being previously sensitized to cinnamyl alcohol via cutaneous exposure (95599).
In a small study of oral Ceylon cinnamon, two patients reported itching (104520). In another small study, two patients reported rashes (108263).
Topically, cinnamon oil can cause skin irritation and allergic dermatitis, probably due to cinnamaldehyde which makes up 60% to 80% of cinnamon oil (2537,12635,92071,95596,95599). In one case report, a 16-year-old female experienced worsening dermatitis after using a homemade facial scrub containing cinnamon powder (type not specified). Symptoms improved after discontinuation of the scrub (95596). Several cases of intraoral allergic contact dermatitis have been reported in patients consuming cinnamon (type not specified) or using products containing constituents of cinnamon (95598).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, gastrointestinal side effects such as heartburn, nausea, bloating, and dyspepsia have been reported (97250).
Hematologic ...Orally, a case of postoperative hemorrhage is reported in a 49-year-old patient after taking Ceylon cinnamon 1 tablespoon daily for 10 months. One day post-colectomy, the patient had an INR of 1.59 and intraabdominal bleeding that required exploratory laparotomies, blood transfusion, and fresh frozen plasma. Ultimately, the patient was discharged (112421).
Hepatic ...While there is concern about the coumarin content in cassia cinnamon increasing the risk for hepatic adverse effects and bleeding, the amount of coumarin in Ceylon cinnamon is negligible and unlikely to cause toxic effects (89652,92072,92073). In one case report, a 73-year-old female taking rosuvastatin for several months developed elevated liver function tests (LFTs), abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting after taking cinnamon (unknown dose and type) for 7 days. The acute hepatitis and elevated LFTs resolved after stopping both cinnamon and rosuvastatin. The patient was later able to resume rosuvastatin without recurrence (97249).
General
...Orally, cranberry seems to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Diarrhea and gastrointestinal discomfort.
Dermatologic ...Orally, skin redness and itching has been reported in one patient (46389).
Gastrointestinal ...In very large doses, for example 3-4 L per day of juice, cranberry can cause gastrointestinal upset and diarrhea, particularly in young children (46364). There are reports of abdominal and gastrointestinal discomfort after taking cranberry tablets, extracts, and juice in clinical trials (16720,46379,111407). Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea have also been reported with consumption of lower doses of cranberry juice cocktail, 16 ounces per day, equivalent to about 4 ounces cranberry juice, for several weeks (16415).
Genitourinary ...Vulvovaginal candidiasis has been associated with ingestion of cranberry juice (46374). Clinical research suggests that ingestion of cranberry juice may be associated with vaginal itching and vaginal dryness (46471). One patient in clinical research stopped taking dried cranberry juice due to excessive urination (46437), and an isolated case of nocturia following ingestion of cranberry tablets has been reported (16720).
Hematologic ...Thrombocytopenia has been reported as an adverse event to cranberry juice (46459).
Other ...An isolated case of sensitive swollen nipples after taking cranberry tablets has been reported (16720).
General
...Orally, elderberry extracts prepared from ripe fruit seem to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: When adverse effects occur, they are likely due to ingestion of raw and unripe elderberries, or seeds, leaves, and other plant parts. Due to cyanogenic glycosides, these may cause nausea, vomiting, severe diarrhea, weakness, dizziness, numbness, and stupor. Cooking eliminates the toxin.
Gastrointestinal
...Orally, nausea and vomiting have been reported after consuming a specific elderberry and echinacea product
Vogel Bioforce AG) (95650). However, it is unclear if this was due to the elderberry or Echinacea contained in the product.
Raw and unripe elderberries, and the seeds, leaves, and other elder tree parts might cause nausea, vomiting, or severe diarrhea due to cyanogenic glycosides (17020,17021). Cooking eliminates the toxin.
Hepatic ...In one case report, a 60-year-old female with underlying autoimmune disease presented with autoimmune hepatitis after taking elderberry at an unknown dose for several years. The patient presented with nausea, jaundice, abdominal pain, and abdominal distention. Liver function tests returned to baseline 4 weeks after initiating treatment with prednisone 40 mg daily and discontinuing elderberry (110123).
Immunologic ...Elder tree pollen might cause an allergic reaction characterized by rhinitis and dyspnea in some patients who are allergic to grass pollen. These patients might also experience an allergic reaction to elderberry extracts (11095).
Neurologic/CNS ...Raw and unripe elderberries might cause weakness, dizziness, numbness, and stupor due to cyanogenic glycosides (17020,17021). Cooking eliminates the toxin.
General
...Orally, the whole fruit, as well as the seed, fruit, and leaf extracts, seem to be well tolerated.
Topically, grape seed extracts seem to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, headache, joint pain, and nausea.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Anaphylaxis to grape skin has been reported.
Dermatologic ...Orally, mild hair thinning has been reported in a patient taking a specific grape leaf extract AS195 KG) (2538). Urticaria (hives) has also been reported with this same extract (53206). Cases of contact dermatitis have been reported in grape workers, including those working in California vineyards (53270,53272,53275).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, abdominal pain and nausea have been reported with use of grape seed extract, but these effects typically occur at rates similar to placebo (9182,13162). In a case report of a 57-year-old man, intermittent nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea occurred over a 10-day period and improved once grape seed extract was stopped (96764). Gastrointestinal adverse effects have also been reported with use of a different grape seed extract (Entelon, Hanlim Pharm). However, the specific types of gastrointestinal effects were not described (100954). A specific grape leaf extract AS195 (Antistax, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG) has reportedly caused flatulence, mild constipation, gastrointestinal discomfort, diarrhea, dyspepsia, dry mouth, and retching (2538,52985,53206). Diarrhea, gastrointestinal distress, indigestion, and aversion to taste have been reported with use of Concord grape juice (52972,53166,53175,53181,53199). Loose stools have been reported in a clinical trial of grape pomace (99270). Bowel obstruction caused by intact grapes and grape seeds has been described in case reports (53241,53284,53278). Excessive consumption of grapes, dried grapes, raisins, or sultanas might cause diarrhea due to laxative effects (4201).
Hematologic ...Orally, one case of leg hematoma following a minor trauma was reported in a person using grape leaf extract (2538). Also, one case of bruising was reported in a person drinking Concord grape juice daily for 2 weeks (52972).
Immunologic ...Orally, there is one report of an anaphylactic reaction to oral grape skin extract, which included urticaria and angioedema (4073).
Musculoskeletal ...Orally, musculoskeletal disorders, including back pain, have been reported with use of a specific grape leaf extract AS195 KG) (2538,53206). Joint pain and lumbago have been reported with use of grape seed extract, but these effects occur at rates similar to placebo (91541).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, headache has been reported with use of grape seed extract, but this effect occurs at rates similar to placebo (9182,91541). A specific grape leaf extract AS195 (Antistax, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG) has reportedly caused dizziness, tiredness, headache, and sleep problems (2538,53206). As a class, nervous system adverse effects have been reported with use of a specific grape seed extract (Entelon, Hanlim Pharm). However, the specific types of adverse neurologic effects were not described (100954).
Ocular/Otic ...Orally, ocular adverse effects have been reported with use of a specific grape seed extract (Entelon, Hanlim Pharm). However, the specific types of ocular adverse effects were not described (100954).
Pulmonary/Respiratory ...Orally, nasopharyngitis and oropharyngeal pain have been reported with use of a specific grape leaf extract AS195 KG) (53206). Sore throat, cough, allergic rhinitis, and nasopharyngitis have been reported with use of grape seed extract, but these effects occur at rates similar to placebo (9182,91541). One case report describes a 16-year-old female who developed increased levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE) following skin-prick exposure to grape vine pollen, as well as positive test responses following bronchial and conjunctival provocation (53301). Reduced forced vital capacity has been described in California grape workers (53080,53081). Occupational eosinophilic lung was diagnosed in a grape grower with a history of asthma. Respiratory exposure to sulfites in grape was implicated as the cause of the adverse reaction (53285).
Other
...Orally, grape products can cause adverse effects due to contamination with pesticides or mycotoxins.
Some evidence has shown that pesticides used in vineyards may remain on grape surfaces post-harvesting. For example, the fungicide folpet sprayed on grapevines has been shown to remain on the grape surface. Although there was minimal penetration of the epicuticular wax, it showed high resistance to washing (52935). Carbaryl has been identified in over 58% of juice samples collected in Canada. This pesticide reportedly occurred more frequently in grape than in other juices. However, estimates of short-term intake were below proposed acute reference doses (53003).
Ochratoxin A is a mycotoxin that is suspected to be nephrotoxic, teratogenic, hepatotoxic and carcinogenic and has been identified in grape juice, frozen grape pulps, and red and white wine sold in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. However, the highest levels identified in grape products were lower than the established virtually safe dose of 5 ng/kg of body weight daily (53010,53004). Ochratoxin A has also been identified in red, but not white, grape juice marketed in Switzerland, Canada, and the U.S. (53292,53020).
General
...Orally, green tea is generally well tolerated when consumed as a beverage in moderate amounts.
Green tea extract also seems to be well tolerated when used for up to 12 months.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Bloating, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, and nausea.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Hepatotoxicity, hypokalemia, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura have been reported rarely.
Cardiovascular
...Acute or short-term oral administration of green tea may cause hypertension (53719,54014,54065,54076,102716).
The risk may be greater for green tea products containing more than 200 mg epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (90161). However, consumption of brewed green tea does not seem to increase blood pressure or pulse, even in mildly hypertensive patients (1451,1452). In fact, some evidence suggests that habitual tea consumption is associated with a reduced risk of developing hypertension (12518). Also, epidemiological research suggests there is no association of caffeine consumption with incidence of hypertension or with cardiovascular disease mortality in patients with hypertension (13739,111027). Rarely, green tea consumption may cause hypotension (53867).
Epidemiological research suggests that regular caffeine intake of up to 400 mg per day, or approximately 8 cups of green tea, is not associated with an increased incidence of atrial fibrillation (38018,38076,91028,91034,97451,97453), atherosclerosis (38033), cardiac ectopy (91127), stroke (37804), ventricular arrhythmia (95948,97453), and cardiovascular disease in general (37805,98806).
Combining ephedra with caffeine can increase the risk of adverse effects. Jitteriness, hypertension, seizures, and temporary loss of consciousness has been associated with the combined use of ephedra and caffeine (2729). There is also a report of ischemic stroke in an athlete who consumed ephedra 40-60 mg, creatine monohydrate 6 grams, caffeine 400-600 mg, and a variety of other supplements daily for 6 weeks (1275). In theory, combining caffeinated green tea with ephedra would have similar effects.
In a case report, the EGCG component of a specific weight loss supplement (Hydroxycut) was thought to be responsible for atrial fibrillation (54028). The patient was given two doses of intravenous diltiazem and was loaded with intravenous digoxin. Thirty-six hours after the last product dose, she spontaneously converted to normal sinus rhythm. The authors suggested that the block of the atrial-specific KCNA5 potassium channel likely played a role in this response.
A case of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura has been reported for a patient who consumed a weight loss product containing green tea (53978). She presented at the emergency department with a one-week history of malaise, fatigue, and petechiae of the skin. Twelve procedures of plasmapheresis were performed, and corticosteroid treatment was initiated. She was discharged after 20 days.
Dermatologic ...Orally, green tea may cause skin rashes or skin irritation (53731,54038,90161,90187,102716). Topically, green tea may cause local skin reactions or skin irritation, erythema, burning, itching, edema, and erosion (53731,54018,97136,104609,111031). A green tea extract ointment applied to the cervix can cause cervical and vaginal inflammation, vaginal irritation, and vulval burning (11310,36442,36438). When applied to external genital or perianal warts, a specific green tea extract ointment (Veregen, Bradley Pharmaceuticals) providing 15% kunecatechins can cause erythema, pruritus, local pain, discomfort and burning, ulceration, induration, edema, and vesicular rash (15067,53907).
Endocrine
...There is some concern that, due to its caffeine content, green tea may be associated with an increased risk of fibrocystic breast disease, breast cancer, and endometriosis.
However, this is controversial since findings are conflicting (8043). Restricting caffeine in females with fibrocystic breast conditions doesn't seem to affect breast nodularity, swelling, or pain (8996).
A population analysis of the Women's Health Initiative observational study has found no association between consumption of caffeine-containing beverages, such as green tea, and the incidence of invasive breast cancer in models adjusted for demographic, lifestyle, and reproductive factors (108806). Also, a dose-response analysis of 2 low-quality observational studies has found that high consumption of caffeine is not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer (108807).
A case of hypoglycemia has been reported for a clinical trial participant with type 2 diabetes who used green tea in combination with prescribed antidiabetes medication (54035).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, green tea beverage or supplements can cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal bloating and pain, constipation, dyspepsia, reflux, morning anorexia, increased thirst, flatulence, and diarrhea. These effects are more common with higher doses of green tea or green tea extract, equivalent to 5-6 liters of tea per day (8117,11366,36398,53719,53867,53936,54038,54076,90139,90140)(90161,90175,90187,97131,97136,102716).
Hepatic
...There is concern that some green tea products, especially green tea extracts, can cause hepatotoxicity in some patients.
In 2017, the regulatory agency Health Canada re-issued a warning to consumers about this concern. The updated warning advises patients taking green tea extracts, especially those with liver disease, to watch for signs of liver toxicity. It also urges children to avoid taking products containing green tea extracts (94897). In 2020, the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) formed an expert panel to review concerns of green tea extract-related hepatotoxicity. Based on their findings, USP determined that any products claiming compliance with USP quality standards for green tea extract must include a specific warning on the label stating "Do not take on an empty stomach. Take with food. Do not use if you have a liver problem and discontinue use and consult a healthcare practitioner if you develop symptoms of liver trouble, such as abdominal pain, dark urine, or jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)" (102722).
Numerous case reports of hepatotoxicity, primarily linked to green tea extract products taken in pill form, have been published. A minimum of 29 cases have been deemed at least probably related to green tea and 38 have been deemed possibly related. In addition, elevated liver enzymes have been reported in clinical research (14136,15026,53740,53746,53775,53859,54027,90139,90162,90164)(93256,94898,94899,102716,102720,102722,107158,111020,111644). Most cases of toxicity have had an acute hepatitis-like presentation with a hepatocellular-elevation of liver enzymes and some cholestasis. Onset of hepatotoxic symptoms usually occurs within 3 months after initiation of the green tea extract supplement, and symptoms can persist from 10 days to 1 year (95439,94897,94898,107158). Some reports of hepatotoxicity have been associated with consumption of green tea-containing beverages as well (15026,53742,54016,90125,90143).
In most cases, liver function returned to normal after discontinuation of the green tea product (14136,15026,53859,93256,107158). In one case, use of a specific ethanolic green tea extract (Exolise, Arkopharma) resulted in hepatotoxicity requiring a liver transplant. Due to concerns about hepatotoxicity, this specific extract was removed from the market by the manufacturer (14310). Since then, at least 5 cases of liver toxicity necessitating liver transplantation have been reported for patients who used green tea extracts (94898,107158). In another case, use of green tea (Applied Nutrition Green Tea Fat Burner) in combination with whey protein, a nutritional supplement (GNC Mega Men Sport), and prickly pear cactus resulted in acute liver failure (90162).
Despite the numerous reports of hepatotoxicity associated with the use of green tea products, the actual number of hepatotoxicity cases is low when the prevalence of green tea use is considered. From 2006 to 2016, liver injury from green tea products was estimated have occurred in only 1 out of 2.7 million patients who used green tea products (94897,95440).
In addition to the fact that green tea hepatotoxicity is uncommon, it is also not clear which patients are most likely to experience liver injury (94897,95440). The hepatotoxicity does not appear to be an allergic reaction or an autoimmune reaction (94897). It is possible that certain extraction processes, for example, ethanolic extracts, produce hepatotoxic constituents. However, in most cases, the presence of contaminants in green tea products has not been confirmed in laboratory analyses (90162).
Although results from one analysis of 4 small clinical studies disagrees (94899), most analyses of clinical data, including one conducted by the European Food Safety Association, found that hepatotoxicity from green tea products is associated with the dose of EGCG in the green tea product. Results show that daily intake of EGCG in amounts greater than or equal to 800 mg per day is associated with a higher incidence of elevated liver enzymes such as alanine transaminase (ALT) (95440,95696,97131). However, it is still unclear what maximum daily dose of EGCG will not increase liver enzyme levels or what minimum daily dose of EGCG begins to cause liver injury. In many cases of liver injury, the dose of green tea extract and/or EGCG is not known. Therefore, a minimum level of green tea extract or EGCG that would cause liver injury in humans cannot be determined (102722). Keep in mind that daily intake of green tea infusions provides only 90-300 mg of EGCG daily. So for a majority of people, green tea infusions are likely safe and unlikely to cause liver injury (95696). Also, plasma levels of EGCG are increased when green tea catechins are taken in the fasting state, suggesting that green tea extract should be taken with food (102722).
Until more is known, advise patients that green tea products, especially those containing green tea extract, might cause liver damage. However, let them know that the risk is uncommon, and it is not clear which products are most likely to cause the adverse effect or which patients are most likely to be affected. Advise patients with liver disease to consult their healthcare provider before taking products with green tea extract and to notify their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms of liver damage, including jaundice, dark urine, sweating, or abdominal pain (102722).
Immunologic ...Orally, matcha tea has resulted in at least one case of anaphylaxis related to green tea proteins. A 9-year-old male experienced systemic redness and hives, nausea, and anaphylaxis 60 minutes after consuming matcha tea-flavored ice cream (107169). The caffeine found in green tea can also cause anaphylaxis in sensitive individuals, although true IgE-mediated caffeine allergy seems to be relatively rare (11315).
Musculoskeletal
...Orally, the ingestion of the green tea constituent epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) or a decaffeinated green tea polyphenol mixture may cause mild muscle pain (36398).
There is some concern regarding the association between caffeinated green tea products and osteoporosis. Epidemiological evidence regarding the relationship between caffeinated beverages such as green tea and the risk for osteoporosis is contradictory. Caffeine can increase urinary excretion of calcium (2669,10202,11317). Females with a genetic variant of the vitamin D receptor appear to be at an increased risk for the detrimental effect of caffeine on bone mass (2669). However, moderate caffeine intake of less than 400 mg per day, or about 8 cups of green tea, doesn't seem to significantly increase osteoporosis risk in most postmenopausal adults with normal calcium intake (2669,6025,10202,11317).
Neurologic/CNS
...Orally, green tea can cause central nervous system stimulation and adverse effects such as headache, anxiety, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, agitation, tremors, restlessness, and confusion.
These effects are more common with higher doses of green tea or green tea extract, equivalent to 5-6 liters of tea per day (8117,11366,53719,90139,102716). The green tea constituent epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) or decaffeinated green tea may also cause mild dizziness and headache (36398).
Combining ephedra with caffeine can increase the risk of adverse effects. Jitteriness, hypertension, seizures, temporary loss of consciousness, and hospitalization requiring life support has been associated with the combined use of ephedra and caffeine (2729).
Topically, green tea extract (Polyphenon E ointment) may cause headache when applied to the genital area (36442).
Psychiatric ...Green tea contains a significant amount of caffeine. Chronic use, especially in large amounts, can produce tolerance, habituation, and psychological dependence (11832). The existence or clinical importance of caffeine withdrawal is controversial. Some researchers think that if it exists, it appears to be of little clinical significance (11839). Other researchers suggest symptoms such as headache; tiredness and fatigue; decreased energy, alertness, and attentiveness; drowsiness; decreased contentedness; depressed mood; difficulty concentrating; irritability; and lack of clear-headedness are typical of caffeine withdrawal (13738). Withdrawal symptoms such as delirium, nausea, vomiting, rhinorrhea, nervousness, restlessness, anxiety, muscle tension, muscle pains, and flushed face have been described. However, these symptoms may be from nonpharmacological factors related to knowledge and expectation of effects. Clinically significant symptoms caused by caffeine withdrawal may be uncommon (2723,11839).
Pulmonary/Respiratory ...A case of granulomatous alveolitis with lymph follicles has been reported for a 67-year-old female who used green tea infusions to wash her nasal cavities for 15 years (54088). Her symptoms disappeared 2 months after stopping this practice and following an undetermined course of corticosteroids. In a case report, hypersensitivity pneumonitis was associated with inhalation of catechin-rich green tea extracts (54025). Occupational exposure to green tea dust can cause sensitization, which may include nasal and asthmatic symptoms (11365).
Renal ...There are two cases of hypokalemia associated with drinking approximately 8 cups daily of green tea in an elderly couple of Asian descent. The hypokalemia improved after reducing their intake by 50%. It is possible that this was related to the caffeine in the green tea (98418).
Other ...Orally, intake of a specific green tea extract product (Polyphenon E) may cause weight gain (90139).
General
...Orally, guarana is typically well tolerated when used in moderation.
Due to its caffeine content, use of large doses may be unsafe.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Stomach burning and nausea.
Cardiovascular
...Orally, a case of premature ventricular contraction has been reported for a 51-year-old female who used guarana as part of a multi-ingredient herbal product (54372).
Guarana contains caffeine. Although acute administration of caffeine can increase blood pressure, regular consumption does not seem to increase either blood pressure or pulse, even in mildly hypertensive patients (1451,1452,2722). Also, epidemiological research suggests there is no association between caffeine consumption and increased incidence of hypertension. Habitual coffee consumption doesn't seem to be related to hypertension, but habitual consumption of sugared or diet cola is associated with development of hypertension (13739).
Combining ephedra with guarana can increase the risk of adverse effects. Cases of hypertension and chest pain have been reported for patients who took products containing guarana and ephedra (8644,54376). A case of cerebral infarction has also been reported for a patient consuming ephedra extract and guarana (48746). There is also a report of ischemic stroke in an athlete who consumed ephedra 40-60 mg, creatine monohydrate 6 grams, caffeine 400-600 mg, and a variety of other supplements daily for six weeks (1275).
Dermatologic ...Guarana contains caffeine. There are several case reports of urticaria after caffeine ingestion (36546,36448,36475).
Endocrine
...Guarana contains caffeine.
Some evidence shows caffeine is associated with fibrocystic breast disease, breast cancer, and endometriosis; however, this is controversial since findings are conflicting (8043). Restricting caffeine in people with fibrocystic breast conditions doesn't seem to affect breast nodularity, swelling, or pain (8996). A population analysis of the Women's Health Initiative observational study has found no association between consumption of caffeine-containing beverages and the incidence of invasive breast cancer in models adjusted for demographic, lifestyle, and reproductive factors (108806). Also, a dose-response analysis of 2 low-quality observational studies has found that high consumption of caffeine is not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer (108807).
Although the effects of guarana alone are not clear, the combination of guarana along with ephedra has been reported to cause increased blood glucose levels and decreased blood levels of potassium (54376).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, guarana can cause a sensation of burning in the stomach and vomiting (54414,91487). These effects may be due to caffeine in guarana. Orally, caffeine can cause gastric irritation, nausea, and vomiting (11832,11838,13735). In infants, caffeine may also cause feeding intolerance and gastrointestinal irritation (6023).
Immunologic ...Guarana contains caffeine. When taken orally, caffeine can cause anaphylaxis in sensitive individuals, although true IgE-mediated caffeine allergy seems to be relatively rare (11315).
Musculoskeletal
...In a clinical trial of guarana extract, one person abandoned treatment due to symptoms of arthritis with edema.
It is not clear if this adverse effect is due to guarana (91487).
Cases of rhabdomyolysis and myoglobinuria have been reported in individuals that have taken products containing guarana in combination with ephedra and other herbal products. These adverse effects are thought to be related to the caffeine content of guarana (19154,36466).
Epidemiological evidence regarding the relationship between caffeine use and the risk for osteoporosis is contradictory. Caffeine can increase urinary excretion of calcium (2669,10202,11317). Women identified with a genetic variant of the vitamin D receptor appear to be at an increased risk for the detrimental effect of caffeine on bone mass (2669). However, moderate caffeine intake, less than 300 mg per day, does not seem to significantly increase osteoporosis risk in most postmenopausal women with normal calcium intake (2669,6025,10202,11317).
Neurologic/CNS
...Orally, guarana can cause dizziness (91483).
The caffeine in guarana can cause insomnia (especially in children), nervousness, restlessness, dizziness, tremors, delirium, and convulsions. Other symptoms include headache, anxiety, and agitation (10755,11832,11838,13735,108016).
Taking guarana with ephedra can cause insomnia, irritability, dizziness, and headache (3719). The combination of ephedra and caffeine in guarana might also increase the risk of adverse effects such as jitteriness, seizures, and temporary loss of consciousness (2729,21015).
Ocular/Otic ...Guarana contains caffeine. When taken orally, caffeine can cause ringing in the ears (11832,11838,13735).
Psychiatric ...In a clinical trial, depression was reported by one person taking guarana extract (91483).
Renal ...Guarana contains caffeine. When taken orally, caffeine can cause diuresis (11832,11838,13735).
Other ...Guarana contains caffeine. The existence or clinical importance of caffeine withdrawal is controversial. Some researchers think that if it exists, it appears to be of little clinical significance (11839). Other researchers suggest symptoms such as headache; tiredness and fatigue; decreased energy, alertness, and attentiveness; drowsiness; decreased contentedness; depressed mood; difficulty concentrating; irritability; and lack of clear-headedness are typical of caffeine withdrawal (13738). Withdrawal symptoms such as delirium, nausea, vomiting, rhinorrhea, nervousness, restlessness, anxiety, muscle tension, muscle pains, and flushed face have been described. However, these symptoms may be from nonpharmacological factors related to knowledge and expectation of effects. Clinically significant symptoms caused by caffeine withdrawal may be uncommon (2723,11839).
General
...Orally, hawthorn seems to be well tolerated when used appropriately.
Topically, no adverse effects have been reported, although a thorough evaluation of safety outcomes has not been conducted.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Multiorgan hypersensitivity reactions resulting in acute renal failure have been reported rarely.
Cardiovascular
...Orally, tachycardia (with facial pains) of uncertain relationship to hawthorn was reported in a multicenter clinical trial (54640).
Palpitations (19244) were reported in three patients in a large surveillance trial of 3,664 patients with cardiac failure (54692) and in 11 patients with congestive heart failure (CHF) in a literature review of 5,577 patients (19247). Circulation failure has been reported in two patients with CHF in a literature review of 5,577 patients (19247). Incidences of hospitalization, hospitalization due to CHF, worsening of CHF, angina, and atrial fibrillation have also been reported with the use of hawthorn extract WS 1442 (Crataegutt forte), although it is unclear if these events are related to hawthorn supplementation or existing CHF (19222). In clinical trials, chest pain (8281), short-term increases in blood pressure (19240), and other non-specific heart problems (17203) have also been reported following the use of various hawthorn preparations (e.g. WS 1442, Korodin).
Orally, severe bradycardia, bradypnea, and Mobitz type 1 second degree heart block have been reported in a 16-year-old female who consumed Hawthorn root extract. Blood tests indicated plasma digoxin levels in the therapeutic range, despite no history of digoxin use. Medical treatment for digoxin cardiotoxicity did not improve symptoms. Symptoms gradually normalized over 3 days after discontinuation of the product (113112). Similarly, a 40-year-old female presented with bradycardia and elevated plasma digoxin levels after taking hawthorn root extract 196 mg daily for 2 days with no history of digoxin use. Symptoms resolved within 24 hours (113113).
Dermatologic ...Orally, erythematous rash has been reported in patients with CHF in a literature review of 5,577 patients (19247). Non-specific rashes and itching (19222,19243) as well as toxiderma from the fruits of hawthorn (54670) have also been reported.
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, rare abdominal discomfort of uncertain relationship to hawthorn has been reported in a large clinical trial, surveillance study, case reports, and a literature review (19247,54640,54692,113112). Digestive intolerance (19241), diarrhea (19243,113112), flatulence (8281), gastroenteritis (8281), increased bowel movements (19243), obstipation (8281), mild and rare nausea (10144,19247,19244), vomiting (113112), nutritional and metabolic problems (17203), and other non-specific gastrointestinal effects (19222), have also been reported. Furthermore, gastrointestinal hemorrhage has been reported in two patients with CHF in a literature review of 5,577 patients (19247).
Musculoskeletal ...In clinical trials, arthritis (8281), back pain (8281), weakness (19243), and other non-specific musculoskeletal effects (19222) have been reported following the use of various hawthorn preparations g. WS 1442, CKBM-A01). Additionally, in a case report, myalgia has been reported following use of hawthorn root extract (113113).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, headache and dizziness/vertigo were reported in 2 patients in a large surveillance trial of 3,664 patients with cardiac failure (54692), in 15 patients with CHF as reported in a literature review of 5,577 patients (19247), in a varying number of clinical trial participants (8281,19222,19244), and in case reports (113112,113113). Incidences of fainting (19222), fever (17203), and infrequent, mild and transient sleepiness have also been reported (19221,54692).
Psychiatric ...Orally, agitation was reported in a large surveillance trial of 3,664 patients with cardiac failure (54692).
Pulmonary/Respiratory ...Orally, bronchitis has been reported following the use of hawthorn extract WS 1442 (8281), and bradypnea has been reported following the use of hawthorn root extract (113112).
Renal ...A case of multiorgan hypersensitivity reaction and acute renal failure following the consumption of C. orientalis has been reported (54654).
Other ...Flu-like syndrome (8281) and other non-specific infections have been reported following the use of the hawthorn extract WS 1442 (17203,19222). Hawthorn has also been reported to cause nosebleeds (8281,10144).
General ...Orally, no adverse effects have been reported with the medicinal use of maca. However, a thorough evaluation of safety outcomes has not been conducted.
Gastrointestinal ...Consumption of fresh, uncooked maca may cause stomach pain (40231).
General
...Orally, Panax ginseng is generally well tolerated when used for up to 6 months.
There is some concern about the long-term safety due to potential hormone-like effects.
Topically, no adverse effects have been reported when ginseng is used as a single ingredient. However, a thorough evaluation of safety outcomes has not been conducted.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Insomnia.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Anaphylaxis, arrhythmia, ischemia, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Cardiovascular ...Panax ginseng may cause hypertension, hypotension, and edema when used orally in high doses, long-term (3353). However, single doses of Panax ginseng up to 800 mg are not associated with changes in electrocardiogram (ECG) parameters or increases in heart rate or blood pressure (96218). There is a case report of menometrorrhagia and tachyarrhythmia in a 39-year-old female who took Panax ginseng 1000-1500 mg/day orally and also applied a facial cream topically that contained Panax ginseng. Upon evaluation for menometrorrhagia, the patient also reported a history of palpitations. It was discovered that she had sinus tachycardia on ECG. However, the patient was a habitual consumer of coffee 4-6 cups/day and at the time of evaluation was also mildly anemic. The patient was advised to discontinue taking Panax ginseng. During the 6 month period following discontinuation the patient did not have any more episodes of menometrorrhagia or tachyarrhythmia (13030). Also, a case of transient ischemic attack secondary to a hypertensive crisis has been reportedly related to oral use of Panax ginseng (89402).
Dermatologic
...Orally, Panax ginseng may cause itching or an allergic response consisting of systemic rash and pruritus (89743,89760,104953,114984,114985).
Skin eruptions have also been reported with use of Panax ginseng at high dosage, long-term (3353). Uncommon side effects with oral Panax ginseng include Stevens-Johnson syndrome (596).
In one case report, a 6-year-old male with a previous diagnosis of generalized pustular psoriasis, which had been in remission for 18 months, presented with recurrent pustular lesions after consuming an unspecified dose of Panax ginseng. The patient was diagnosed with pityriasis amiantacea caused by subcorneal pustular dermatosis. Treatment with oral dapsone 25 mg daily was initiated, and symptoms resolved after 4 weeks (107748). In another case report, a 26-year-old female presented with itchy exanthem and oval erythematous lesions on the face, neck, and abdomen after consuming a decoction containing Panax ginseng, aconite, ginger, licorice, Cassia cinnamon, goldthread, and peony 400 mL twice daily for 1 week. Pityriasis rosea-like eruption was suspected, but the patient refused topical or oral antihistamines or corticosteroids. The patient continued taking the decoction but with Panax ginseng and aconite removed. After 6 days, symptoms began to resolve, and by 17 days symptom improvement was significant (114986). It is unclear if this reaction was due to Panax ginseng, aconite, the combination, or some other factor. Pityriasis rosea typically resolves spontaneously.
Topically, when a specific multi-ingredient cream preparation (SS Cream) has been applied to the glans penis, mild pain, local irritation, and burning have occurred (2537).
Endocrine
...The estrogenic effects of ginseng are controversial.
Some clinical evidence suggests it doesn't have estrogen-mediated effects (10981). However, case reports of ginseng side effects such as postmenopausal vaginal bleeding suggest estrogenic activity (590,591,592,10982,10983).
In a 12-year-old Korean-Japanese male, enlargement of both breasts with tenderness in the right breast (gynecomastia) occurred after taking red ginseng extract 500 mg daily orally for one month. Following cessation of the product, there was no further growth or pain (89733). Swollen and tender breasts also occurred in a 70-year-old female using Panax ginseng orally (590).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, Panax ginseng can cause decreased appetite (3353), constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia (3353,89734,103477,112841,114980,114985), abdominal pain (89734,87984,112841,114985), and nausea (589,87984). However, these effects are typically associated with long-term, high-dose usage (3353). Some evidence suggests that fermented Panax ginseng is more likely to cause abdominal pain and diarrhea when compared with unfermented Panax ginseng (112841).
Genitourinary
...Amenorrhea has been reported with oral use of Panax ginseng (3353).
Topically, when a specific multi-ingredient cream preparation (SS Cream) has been applied to the glans penis, sporadic erectile dysfunction and excessively delayed ejaculation have occurred (2537). Less commonly, patients can experience vaginal bleeding (591,592,3354,23630).
Hepatic ...It is unclear if Panax ginseng is associated with adverse hepatic effects. Cholestatic hepatitis has been reported in a 65-year old male following oral use of a combination product containing Panax ginseng and other ingredients (Prostata). However, it is unclear if this adverse effect was due to Panax ginseng, other ingredients, or the combination (598). An elevation in liver enzymes has been rarely reported in clinical research (114985).
Immunologic ...A case of anaphylaxis, with symptoms of hypotension and rash, has been reported following ingestion of a small amount of Panax ginseng syrup (11971).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, one of the most common side effects to Panax ginseng is insomnia (589,89734,111336,114985). Headache (594,23638,112840,114985), vertigo, euphoria, and mania (594) have also been reported. Migraine and somnolence occurred in single subjects in a clinical trial (87984). In a case report of a 46-year-old female, orobuccolingual dyskinesia occurred following oral use of a preparation containing black cohosh 20 mg and Panax ginseng 50 mg twice daily for menopausal symptoms. The patient's condition improved once the product was stopped and treatment with baclofen 40 mg and clonazepam 20 mg daily was started (89735).
General
...Orally and topically, royal jelly seems to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Dyspnea, eczema, oral allergy syndrome, pruritus, and urticaria in people with a history of asthma or atopy.
Topically: Contact dermatitis and skin irritation.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Anaphylaxis, status asthmaticus, and death in people with a history of asthma or atopy.
Gastrointestinal ...There is one case report of hemorrhagic colitis with abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea with concomitant hemorrhagic and edematous mucosa of the sigmoid colon after ingestion of royal jelly. Symptoms resolved within 2 weeks following discontinuation of royal jelly and conservative treatment (3516).
Immunologic
...In people with a history of atopy or asthma, royal jelly taken orally appears to cause a high rate of allergic symptoms including pruritus, urticaria, eczema, eyelid and facial edema, conjunctivitis, rhinorrhea, dyspnea, oral allergy syndrome, and asthma (7314,7315,7316,10623,95872).
In severe cases, royal jelly can cause status asthmaticus, anaphylaxis, and death (792,7315,7316,10623,10624,108511). Allergic symptoms are associated with IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions (3513,10623).
Topically, skin irritation, exacerbation of dermatitis, or contact dermatitis may occur (791).
From occupational exposure, royal jelly can cause allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and asthma (95868).
Neurologic/CNS ...There is one report of dizziness in a patient who took a combination product containing royal jelly, bee pollen extract, and a bee pollen plus pistil extract (12008).
General
...Orally, sodium is well tolerated when used in moderation at intakes up to the Chronic Disease Risk Reduction (CDRR) intake level.
Topically, a thorough evaluation of safety outcomes has not been conducted.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Worsened cardiovascular disease, hypertension, kidney disease.
Cardiovascular
...Orally, intake of sodium above the CDRR intake level can exacerbate hypertension and hypertension-related cardiovascular disease (CVD) (26229,98176,100310,106263).
A meta-analysis of observational research has found a linear association between increased sodium intake and increased hypertension risk (109398). Observational research has also found an association between increased sodium salt intake and increased risk of CVD, mortality, and cardiovascular mortality (98177,98178,98181,98183,98184,109395,109396,109399). However, the existing research is unable to confirm a causal relationship between sodium intake and increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality; high-quality, prospective research is needed to clarify this relationship (100312). As there is no known benefit with increased salt intake that would outweigh the potential increased risk of CVD, advise patients to limit salt intake to no more than the CDRR intake level (100310).
A reduction in sodium intake can lower systolic blood pressure by a small amount in most individuals, and diastolic blood pressure in patients with hypertension (100310,100311,106261). However, post hoc analysis of a small crossover clinical study in White patients suggests that 24-hour blood pressure variability is not affected by high-salt intake compared with low-salt intake (112910). Additionally, the available research is insufficient to confirm that a further reduction in sodium intake below the CDRR intake level will lower the risk for chronic disease (100310,100311). A meta-analysis of clinical research shows that reducing sodium intake increases levels of total cholesterol and triglycerides, but not low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, by a small amount (106261).
It is unclear whether there are safety concerns when sodium is consumed in amounts lower than the adequate intake (AI) levels. Some observational research has found that the lowest levels of sodium intake might be associated with increased risk of death and cardiovascular events (98181,98183). However, this finding has been criticized because some of the studies used inaccurate measures of sodium intake, such as the Kawasaki formula (98177,98178,101259). Some observational research has found that sodium intake based on a single 24-hour urinary measurement is inversely correlated with all-cause mortality (106260). The National Academies Consensus Study Report states that there is insufficient evidence from observational studies to conclude that there are harmful effects from low sodium intake (100310).
Endocrine ...Orally, a meta-analysis of observational research has found that higher sodium intake is associated with an average increase in body mass index (BMI) of 1. 24 kg/m2 and an approximate 5 cm increase in waist circumference (98182). It has been hypothesized that the increase in BMI is related to an increased thirst, resulting in an increased intake of sugary beverages and/or consumption of foods that are high in salt and also high in fat and energy (98182). One large observational study has found that the highest sodium intake is not associated with overweight or obesity when compared to the lowest intake in adolescents aged 12-19 years when intake of energy and sugar-sweetened beverages are considered (106265). However, in children aged 6-11 years, usual sodium intake is positively associated with increased weight and central obesity independently of the intake of energy and/or sugar-sweetened beverages (106265).
Gastrointestinal ...In one case report, severe gastritis and a deep antral ulcer occurred in a patient who consumed 16 grams of sodium chloride in one sitting (25759). Chronic use of high to moderately high amounts of sodium chloride has been associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer (29405).
Musculoskeletal
...Observational research has found that low sodium levels can increase the risk for osteoporosis.
One study has found that low plasma sodium levels are associated with an increased risk for osteoporosis. Low levels, which are typically caused by certain disease states or chronic medications, are associated with a more than 2-fold increased odds for osteoporosis and bone fractures (101260).
Conversely, in healthy males on forced bed rest, a high intake of sodium chloride (7.7 mEq/kg daily) seems to exacerbate disuse-induced bone and muscle loss (25760,25761).
Oncologic ...Population research has found that high or moderately high intake of sodium chloride is associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer when compared with low sodium chloride intake (29405). Other population research in patients with gastric cancer has found that a high intake of sodium is associated with an approximate 65% increased risk of gastric cancer mortality when compared with a low intake. When zinc intake is taken into consideration, the increased risk of mortality only occurred in those with low zinc intake, but the risk was increased to approximately 2-fold in this sub-population (109400).
Pulmonary/Respiratory ...In patients with hypertension, population research has found that sodium excretion is modestly and positively associated with having moderate or severe obstructive sleep apnea. This association was not found in normotensive patients (106262).
Renal ...Increased sodium intake has been associated with impaired kidney function in healthy adults. This effect seems to be independent of blood pressure. Observational research has found that a high salt intake over approximately 5 years is associated with a 29% increased risk of developing impaired kidney function when compared with a lower salt intake. In this study, high salt intake was about 2-fold higher than low salt intake (101261).
General
...Orally, stevia and steviol glycosides appear to be well tolerated.
Most minor adverse effects seem to resolve after the first week of use.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Abdominal bloating, dizziness, headache, myalgia, nausea, and numbness.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Allergic reactions.
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, stevia and steviol glycosides such as stevioside, can cause gastrointestinal adverse effects such as abdominal fullness and nausea. However, these generally resolve after the first week of use (11809,11810,113005).
Immunologic ...Theoretically, stevia might cause allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to plants in the Asteraceae/Compositae family (11811). Members of this family include ragweed, chrysanthemums, marigolds, daisies, and many other herbs.
Musculoskeletal ...Orally, stevia and steviol glycosides may cause myalgia, but this generally resolves after the first week of use (11809,11810).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, stevia and steviol glycosides may cause headache, dizziness, and numbness (11809,11810).
General
...Orally, there is limited information available about the adverse effects of yohimbe.
Yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, might be unsafe; most reported adverse effects are dose-related.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, has been associated with anxiety, agitation, diaphoresis, diarrhea, flushing, headache, hypertension, increased urination, nausea, tachycardia, tremors, vertigo, and vomiting.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, has been associated with atrial fibrillation, hypertensive crisis, myocardial infarction, and QT interval prolongation.
Cardiovascular ...Orally, yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, has been associated with hypertension, especially at higher doses (3312,17465,86801,86802,86804,86811,86820,86822,86834,86856)(86786,86896). A case of hypertensive crisis was reported in a 63-year-old male taking a yohimbine-containing herbal product once daily for one month. The patient was successfully managed with intravenous nitroprusside followed by clonidine (91521). Tachycardia, fluid retention, palpitations, and chest discomfort have also been reported (3312,17465,86786,86793,86801,86802,86804,86822,86843,86854)(86856,86866,86867,86869,86871,86874,86875). Conduction abnormalities have also been reported (86856,86786). There have been some reports of myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, and QT interval prolongation (17465). In theory, these effects may also occur with the use of yohimbe bark extract.
Dermatologic ...Orally, yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, may cause rash, erythrodermic skin eruption, and exanthema (3312,3971,86804,86896,86878).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, may cause nausea, vomiting, increased salivation, diarrhea, and gastrointestinal distress (3970,17465,49902,86780,86781,86786,86801,86804,86824,86827)(86828,86829,86863,86878,86882,86896).
Genitourinary ...Orally, yohimbine may cause dartos contraction or decreased libido in some patients (86786,86882). A case of severe intractable priapism has been reported for a 42-year-old male who took a supplement containing yohimbe extract the previous day for sexual enhancement. Treatment with phenylephrine 400 mcg was unsuccessful at resolving the priapism, so surgical insertion of a proximal cavernosal spongiosum shunt was needed (86804).
Hematologic ...A case of drug-induced agranulocytosis has been reported following prolonged use of oral yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe (86877).
Immunologic ...There is one report of a hypersensitivity reaction including fever; chills; malaise; itchy, scaly skin; progressive renal failure; and lupus-like syndrome associated with ingestion of a one-day dose of yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe (6169).
Musculoskeletal ...Orally, yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, may cause muscle aches (86850).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, has been associated with reports of general central nervous system (CNS) and autonomic excitation, tremulousness, head twitching, seizure threshold changes, enhanced brain norepinephrine release, decreased energy, dizziness, vertigo, and headache (3312,3971,86774,86779,86786,86804,86827,86857,86870,86882)(86883). Cold feet and chills have also been reported with yohimbine (86827,86896). Other adverse reactions include flushing and diaphoresis (17465). Excessive doses of yohimbine can also cause paralysis (11,18). A case of acute neurotoxicity characterized by malaise, vomiting, loss of consciousness, and seizures has been reported for a 37-year-old bodybuilder who ingested a single dose of yohimbine 5 grams. Improvement was seen within 12 hours following treatment with furosemide, labetalol, clonidine, urapidil, and gastrointestinal decontamination (86801).
Psychiatric ...Orally, yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, may increase malaise, fatigue, insomnia, restlessness, agitation, and anxiety (3312,3970,3971,17465,86786,86801,86804,86822,86827,86834)(86868,86878,86882,86896). In a clinical study of healthy subjects, administration of yohimbine increased impulsivity, with larger doses increasing impulsivity more than 50% (86784,86810).
Pulmonary/Respiratory ...Orally, yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, may cause bronchospasm, tachypnea, cough, and rhinorrhea (17465,86825,86850). A case of sinusitis characterized by pain and discomfort above both eyes has been reported for a 59-year-old male taking yohimbine 5.4 mg three times daily to treat erectile dysfunction. Symptoms resolved within 24 hours of discontinuing yohimbine. The effect was attributed to the alpha-2 adrenergic antagonist effects of yohimbine (94112). Excessive doses of yohimbine can cause respiratory depression (1118).
Renal ...Orally, yohimbine, a constituent of yohimbe, may increase urinary frequency (3312,3970,3971,17465,86804,86827,86850,86861,86882). A case of acute renal failure has been reported for a 42-year-old male taking yohimbine. Normalization of renal function was achieved following 2 weeks of treatment with corticosteroids. The renal dysfunction was attributed to yohimbine-induced systemic lupus erythematosus (6169).
